Georeferenced Maps: A Foundation For Spatial Understanding
Georeferenced Maps: A Foundation for Spatial Understanding
Related Articles: Georeferenced Maps: A Foundation for Spatial Understanding
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Georeferenced Maps: A Foundation for Spatial Understanding. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Georeferenced Maps: A Foundation for Spatial Understanding

Georeferenced maps are the cornerstone of spatial analysis, providing a framework for understanding and interacting with the world around us. They are essentially maps that have been precisely linked to a geographic coordinate system, enabling the accurate representation of real-world locations and features. This fundamental connection between map data and the Earth’s surface empowers a wide range of applications, from navigation and resource management to environmental monitoring and urban planning.
Understanding the Essence of Georeferencing
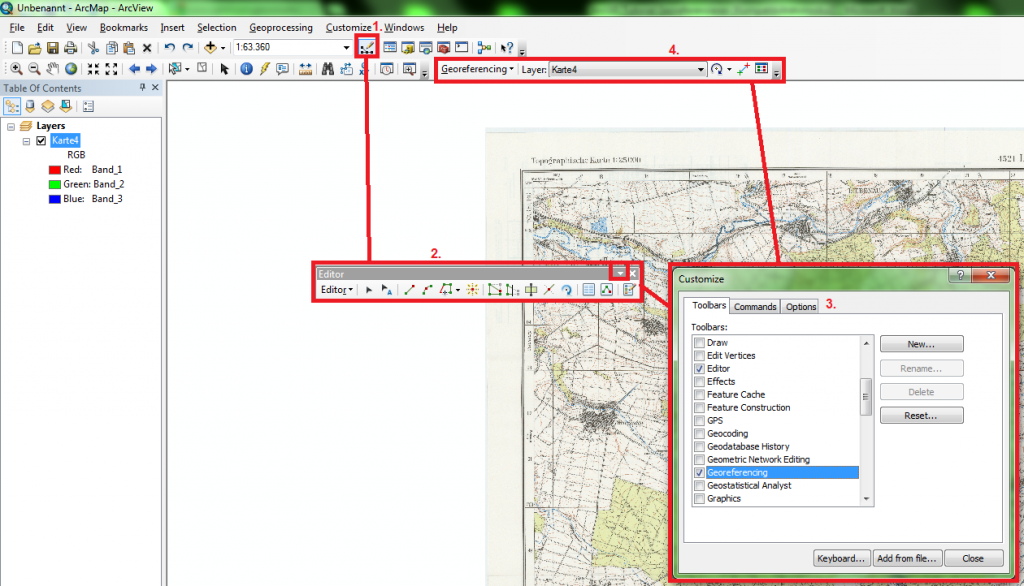
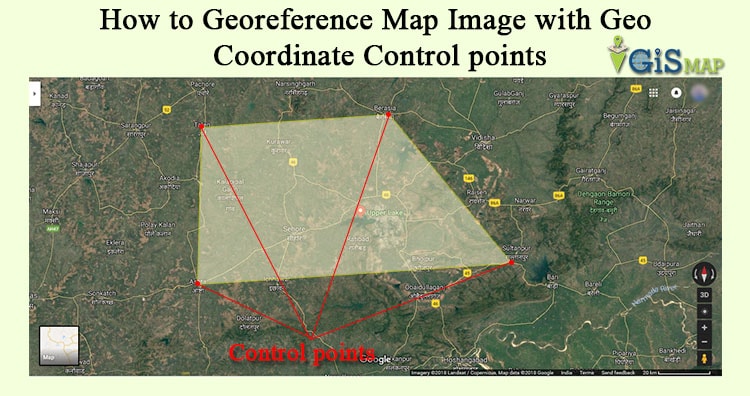
Georeferencing involves aligning map data with a specific coordinate system, typically the widely accepted World Geodetic System (WGS84). This alignment ensures that every point on the map corresponds to a unique geographic location on Earth, expressed in terms of latitude and longitude. The process utilizes reference points, known as ground control points (GCPs), which are identifiable features on both the map and the real world. These GCPs serve as anchors, enabling the map to be accurately transformed and registered onto the Earth’s surface.
Types of Georeferencing
Georeferencing can be achieved through various methods, each tailored to the specific data and application:
- Direct Georeferencing: This method directly assigns coordinates to map features, such as points, lines, or polygons. It is commonly employed for digital maps created from scanned paper maps or aerial photographs.
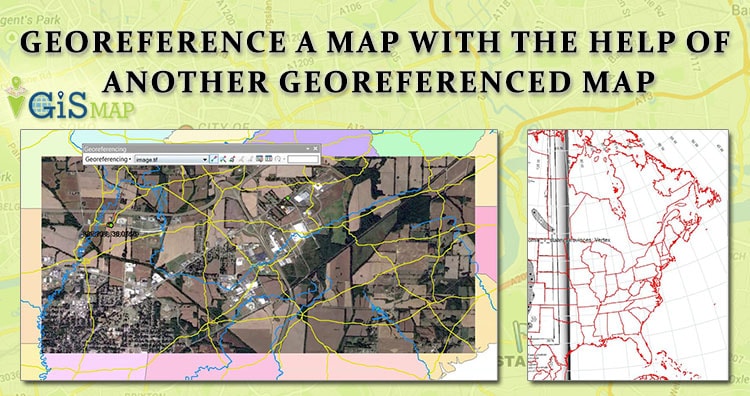
- Indirect Georeferencing: This approach relies on establishing a spatial relationship between the map data and a known geospatial dataset, such as a digital elevation model or satellite imagery. The relationship is determined through geometric transformations, aligning the map to the reference dataset.
- Automatic Georeferencing: Advances in computer vision and machine learning have paved the way for automatic georeferencing techniques. These algorithms can identify and match features between maps and reference datasets, automating the alignment process.
The Benefits of Georeferenced Maps
The integration of geographic coordinates into maps unlocks a multitude of benefits, revolutionizing how we analyze, visualize, and interact with spatial information:
- Accurate Location Information: Georeferenced maps provide precise location data, enabling accurate navigation, resource tracking, and infrastructure planning.
- Spatial Analysis: By linking map features to geographic coordinates, georeferenced maps facilitate spatial analysis, enabling the study of patterns, relationships, and trends across geographic areas.
- Data Integration and Overlaying: Georeferenced maps allow for the seamless integration and overlay of various datasets, such as population density, soil types, or environmental data, creating comprehensive spatial representations.
- Visualization and Communication: Georeferenced maps enhance visualization and communication of spatial information, making complex data accessible and understandable to a wider audience.
- Decision-Making Support: By providing a spatial context for data, georeferenced maps empower informed decision-making in diverse fields, including urban planning, disaster management, and environmental conservation.
Applications of Georeferenced Maps
The applications of georeferenced maps are vast and diverse, spanning across various industries and disciplines:
- Navigation and Mapping: Georeferenced maps are the foundation of navigation systems, enabling precise route planning and location tracking. They are integral to GPS devices, mapping applications, and online navigation platforms.
- Resource Management: Georeferenced maps play a crucial role in resource management, facilitating the mapping and monitoring of natural resources, such as forests, water bodies, and mineral deposits.
- Environmental Monitoring: Georeferenced maps are essential for environmental monitoring, enabling the tracking of land use changes, pollution levels, and climate change impacts.
- Urban Planning: Georeferenced maps support urban planning by providing a framework for analyzing population distribution, infrastructure development, and land use patterns.
- Disaster Management: Georeferenced maps are critical for disaster response and preparedness, enabling the assessment of damage, evacuation planning, and resource allocation.
- Agriculture and Forestry: Georeferenced maps are used in precision agriculture, allowing farmers to optimize crop yields, manage irrigation, and monitor soil health.
- Archaeology and History: Georeferenced maps aid in archaeological research, enabling the mapping of ancient sites, cultural landscapes, and historical events.
- Public Health: Georeferenced maps are used in public health to track disease outbreaks, identify vulnerable populations, and allocate healthcare resources.
- Real Estate and Property Management: Georeferenced maps are essential for real estate, facilitating property valuation, site selection, and property boundary identification.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the difference between a georeferenced map and a regular map?
A regular map is a visual representation of an area without a specific coordinate system. It may provide general location information but lacks the precise spatial referencing of a georeferenced map. Georeferenced maps, on the other hand, are linked to a coordinate system, enabling accurate location determination and spatial analysis.
2. How can I georeference a map?
Georeferencing a map involves aligning it with a specific coordinate system. This can be done through various methods, including:
- Using ground control points (GCPs): Identifying common features on both the map and a reference dataset, such as satellite imagery or a digital elevation model.
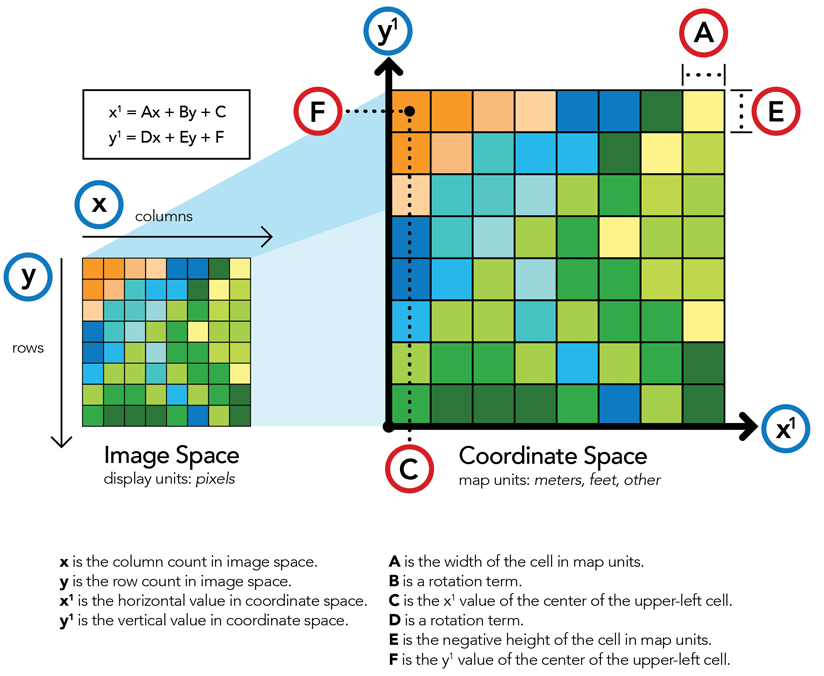
- Utilizing geometric transformations: Applying mathematical functions to align the map with the reference dataset.
- Employing automated georeferencing tools: Utilizing software that automatically identifies and matches features between the map and reference data.
3. What are the different types of coordinate systems used in georeferencing?
Several coordinate systems are commonly used in georeferencing, including:
- Geographic coordinate system (GCS): Uses latitude and longitude to define locations on the Earth’s surface.
- Projected coordinate system (PCS): Transforms geographic coordinates into a planar system, enabling measurements on a flat surface.
- UTM (Universal Transverse Mercator): A widely used projected coordinate system that divides the Earth into 60 zones, each with a specific projection.
4. What are the limitations of georeferenced maps?
Georeferenced maps, while powerful tools, have limitations:
- Accuracy: The accuracy of georeferenced maps depends on the quality of the reference data and the georeferencing process.
- Data resolution: The resolution of the map data can limit the level of detail that can be represented.
- Map projection: Different map projections can distort distances and shapes, affecting the accuracy of measurements.
- Data updates: Georeferenced maps may become outdated as geographic features change over time.
Tips for Using Georeferenced Maps
- Choose the appropriate coordinate system: Select the coordinate system that best suits the specific application and geographic area.
- Use reliable reference data: Ensure that the reference data used for georeferencing is accurate and up-to-date.
- Validate the georeferencing process: Verify the accuracy of the georeferencing by comparing the aligned map with ground truth data.
- Consider data resolution and accuracy: Understand the limitations of the map data in terms of resolution and accuracy.
- Stay informed about data updates: Regularly update the georeferenced maps with new data to maintain accuracy.
Conclusion
Georeferenced maps are powerful tools that bridge the gap between geographic data and the real world. They provide a foundation for spatial analysis, enabling us to understand, analyze, and visualize spatial information with unprecedented accuracy. As technology advances, georeferenced maps are becoming increasingly sophisticated, offering new possibilities for spatial data management, visualization, and decision-making across diverse fields. The importance of georeferenced maps will continue to grow as we strive to understand and interact with the world around us in increasingly complex and interconnected ways.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Georeferenced Maps: A Foundation for Spatial Understanding. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To South Dakota Plat Maps
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Malaysia: A Geographical Exploration
- Navigating The World Of Digital Maps: A Comprehensive Guide To Purchasing Maps Online
- Unlocking The Secrets Of Malvern, Arkansas: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Map
- Uncovering The Treasures Of Southern Nevada: A Comprehensive Guide To The Caliente Map
- Unraveling The Topography Of Mexico: A Comprehensive Look At The Relief Map
- Navigating The Heart Of History: A Comprehensive Guide To The Athens City Map
- Navigating The Beauty Of Greece: A Guide To Printable Maps
Leave a Reply