Mapping The World: A Comprehensive Guide To Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Mapping the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Related Articles: Mapping the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Mapping the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographic Information Systems (GIS). Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographic Information Systems (GIS)

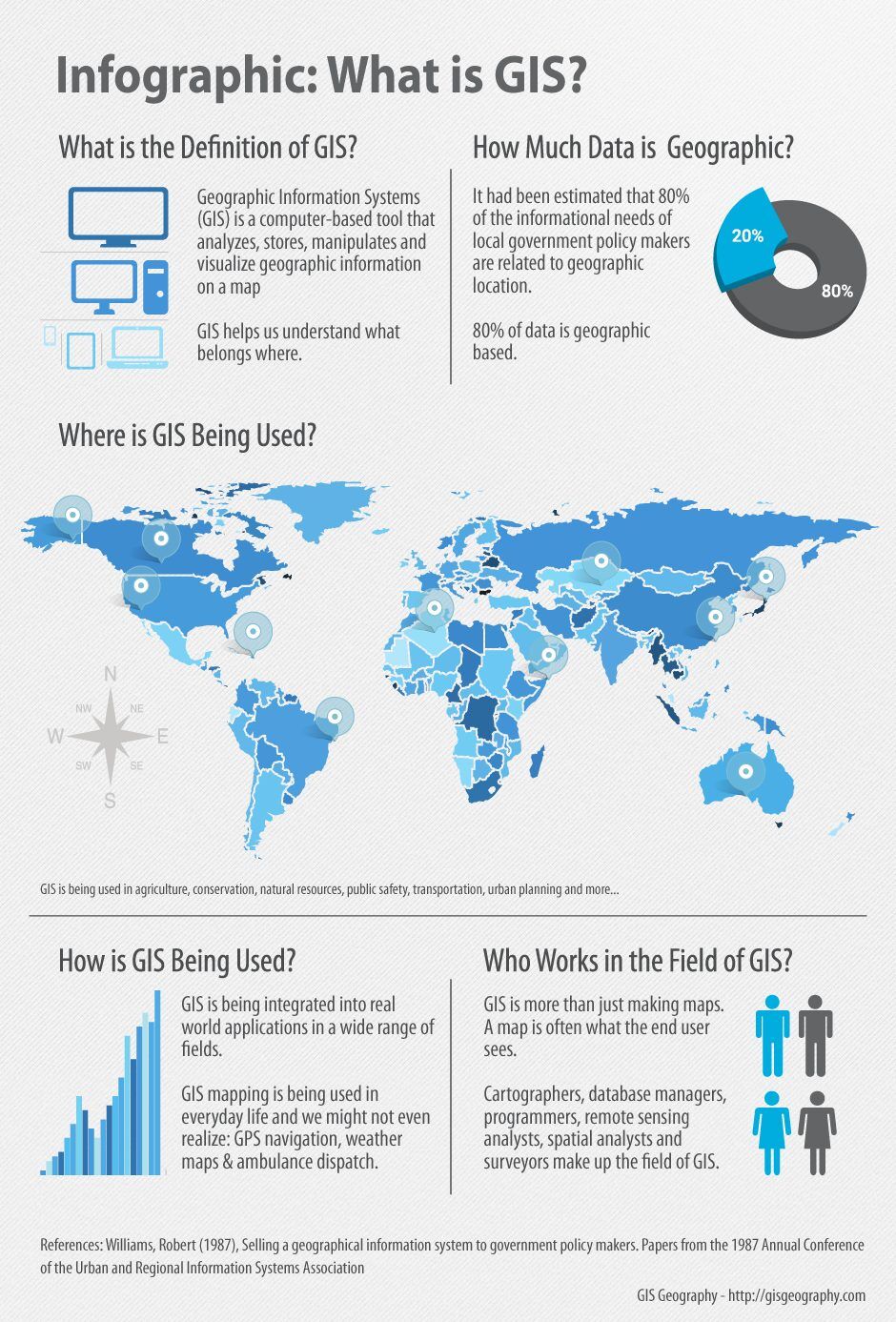
The world is a complex tapestry of interconnected systems, from the natural environment to human societies. Understanding this intricate web requires a powerful tool – Geographic Information Systems (GIS). GIS is a technology that allows us to capture, analyze, and visualize spatial data, providing insights that inform decisions and shape our understanding of the world.
Understanding the Power of GIS
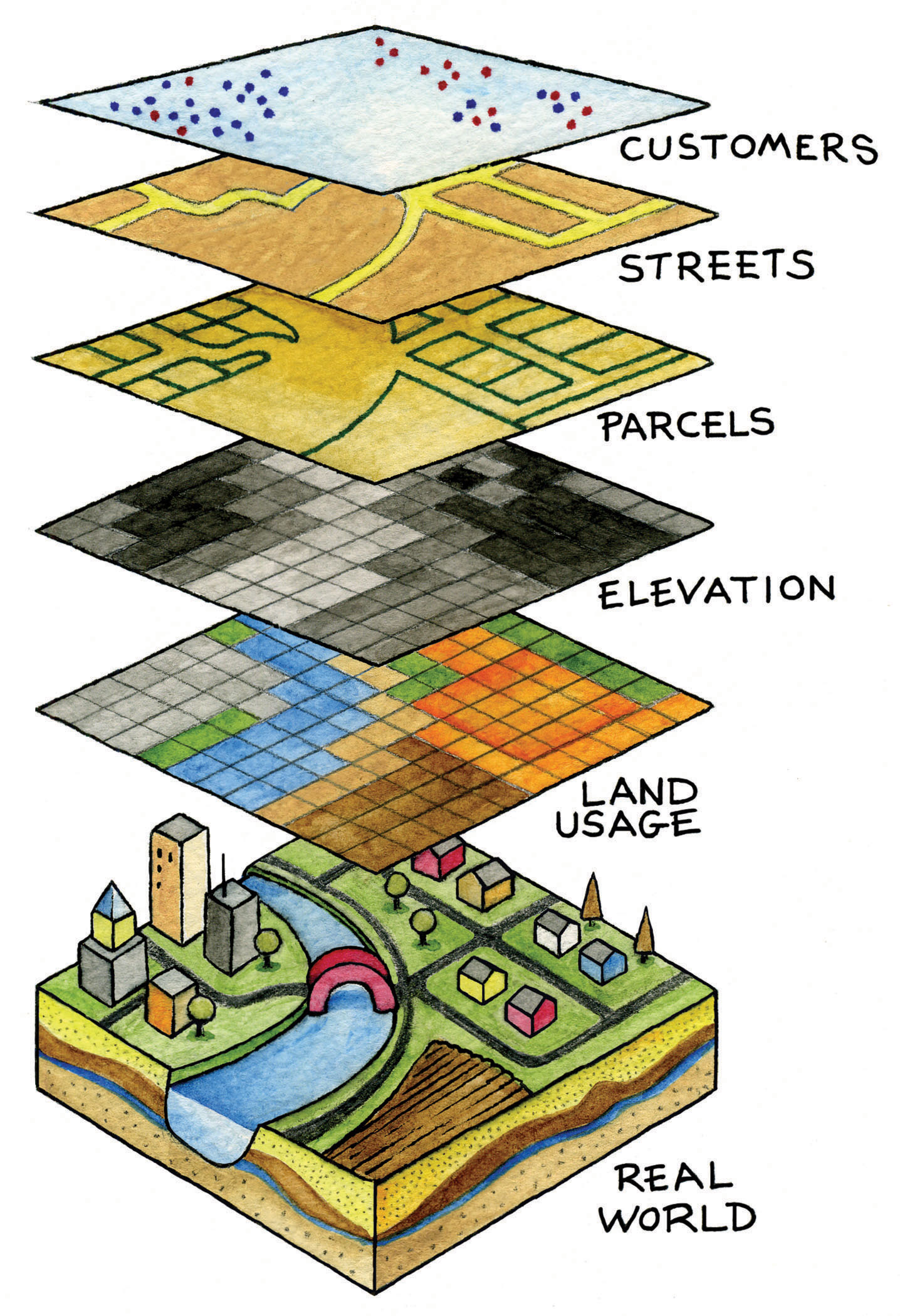
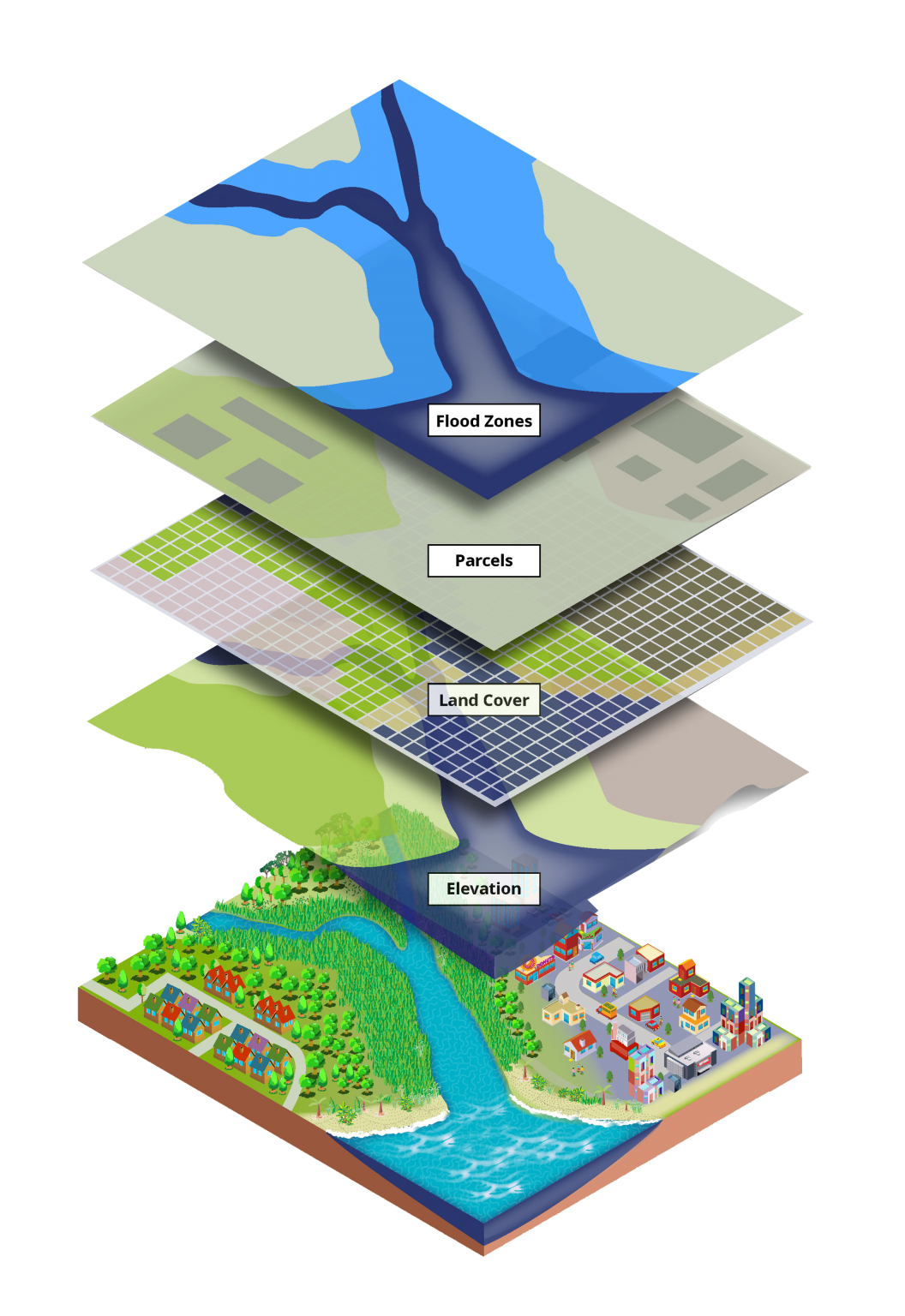
GIS is not merely about creating maps; it’s about transforming data into actionable information. By integrating spatial data with other types of information, GIS enables users to:
- Visualize Patterns and Trends: GIS maps can reveal hidden patterns and trends in data that might otherwise go unnoticed. For instance, visualizing crime data alongside socioeconomic indicators can help identify areas with higher crime rates and understand potential contributing factors.
- Analyze Relationships and Interactions: GIS allows for analyzing the relationships between different spatial elements. This can be applied to diverse fields, such as understanding how deforestation impacts water resources or how infrastructure development affects urban sprawl.
- Make Informed Decisions: By providing a holistic view of spatial information, GIS empowers decision-makers with valuable insights. This can range from optimizing transportation routes to identifying optimal locations for new schools or hospitals.
- Communicate Complex Information Effectively: GIS maps serve as a powerful communication tool, making complex spatial data easily accessible and understandable to a wider audience.
Key Components of GIS
GIS systems are composed of several key components:
- Hardware: This includes computers, servers, and mobile devices that provide the platform for running GIS software.
- Software: GIS software provides the tools for capturing, managing, analyzing, and visualizing spatial data. Popular options include ArcGIS, QGIS, and MapInfo.
- Data: GIS relies on geospatial data, which represents geographic features and their attributes. This data can be obtained from various sources, including satellite imagery, aerial photographs, maps, and sensor networks.
- People: GIS professionals, including analysts, technicians, and specialists, are crucial for designing, implementing, and interpreting GIS solutions.
Applications of GIS Across Diverse Fields
GIS has become an indispensable tool across a wide range of fields, including:
- Environmental Management: GIS helps monitor environmental changes, track biodiversity, assess pollution levels, and manage natural resources.
- Urban Planning: GIS supports urban planning by analyzing population density, transportation networks, infrastructure needs, and land use patterns.
- Disaster Management: GIS plays a crucial role in disaster preparedness, response, and recovery by providing real-time information on affected areas, evacuation routes, and resource allocation.
- Agriculture: GIS assists farmers in optimizing crop yields, managing soil health, and tracking livestock movements.
- Healthcare: GIS helps analyze disease outbreaks, identify vulnerable populations, and optimize healthcare facility locations.
- Business and Marketing: GIS supports businesses in identifying target markets, optimizing logistics, and analyzing customer behavior.
The Future of GIS: Emerging Trends
The field of GIS is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and growing demands for spatial data analysis. Some key trends shaping the future of GIS include:
- Cloud-based GIS: Cloud computing enables access to powerful GIS tools and data storage on demand, enhancing accessibility and scalability.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration: AI algorithms are being integrated into GIS systems to automate data analysis, improve predictive modeling, and enhance spatial decision-making.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Connectivity: The integration of sensors and other IoT devices with GIS allows for real-time data collection and monitoring, enabling more dynamic and responsive applications.
- 3D GIS: The development of 3D GIS platforms allows for visualizing and analyzing spatial data in a more realistic and immersive way, providing deeper insights and better communication.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about GIS
Q: What is the difference between GIS and GPS?
A: GPS (Global Positioning System) is a technology that uses satellites to determine precise location coordinates. GIS, on the other hand, is a system for managing, analyzing, and visualizing spatial data, which includes GPS coordinates but goes beyond simply locating points.
Q: What are some common GIS software applications?
A: Some popular GIS software applications include ArcGIS, QGIS, MapInfo, and Google Earth Pro. Each offers different features and functionalities, catering to various user needs.
Q: How can I learn more about GIS?
A: There are numerous resources available for learning about GIS. Online courses, university programs, and professional certifications can provide comprehensive knowledge and skills.
Q: What are some career opportunities in GIS?
A: GIS professionals are in high demand across various sectors. Potential career paths include GIS analyst, geospatial data scientist, cartographer, and environmental planner.
Tips for Using GIS Effectively
- Define your goals: Clearly articulate the objectives you want to achieve with GIS analysis.
- Choose the right data: Ensure the data you use is accurate, relevant, and appropriate for your analysis.
- Understand data limitations: Be aware of potential biases or inaccuracies in the data you use.
- Visualize data effectively: Use maps and other visualization tools to communicate your findings clearly and effectively.
- Collaborate with others: GIS projects often involve collaboration with experts from different fields.
Conclusion
GIS has revolutionized our ability to understand and interact with the world around us. By harnessing the power of spatial data analysis, GIS empowers us to make informed decisions, solve complex problems, and create a more sustainable and equitable future. As technology continues to evolve, GIS will undoubtedly play an even greater role in shaping our world.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographic Information Systems (GIS). We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To South Dakota Plat Maps
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Malaysia: A Geographical Exploration
- Navigating The World Of Digital Maps: A Comprehensive Guide To Purchasing Maps Online
- Unlocking The Secrets Of Malvern, Arkansas: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Map
- Uncovering The Treasures Of Southern Nevada: A Comprehensive Guide To The Caliente Map
- Unraveling The Topography Of Mexico: A Comprehensive Look At The Relief Map
- Navigating The Heart Of History: A Comprehensive Guide To The Athens City Map
- Navigating The Beauty Of Greece: A Guide To Printable Maps
Leave a Reply