Navigating The Peaks: Understanding And Utilizing Peak-to-Peak Maps
Navigating the Peaks: Understanding and Utilizing Peak-to-Peak Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Peaks: Understanding and Utilizing Peak-to-Peak Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Peaks: Understanding and Utilizing Peak-to-Peak Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Peaks: Understanding and Utilizing Peak-to-Peak Maps
In the realm of data visualization and analysis, peak-to-peak maps, also known as range maps, emerge as powerful tools for understanding and interpreting trends. These maps, distinguished by their unique representation of data, offer a compelling visual narrative, highlighting the highs and lows within a given dataset.
Unveiling the Essence of Peak-to-Peak Maps
Peak-to-peak maps are a specialized type of cartographic representation that emphasizes the difference between the highest and lowest values within a defined area. Unlike traditional maps that focus on absolute values, these maps prioritize the range or variation of data, providing a visual understanding of the extent of change.
The Mechanics of Visualizing Data Ranges
The core principle behind peak-to-peak maps lies in the use of color gradients or shading to depict the range of values. The color scale typically starts with a lighter shade representing the lowest value and transitions to a darker shade representing the highest value. The variation in color intensity across the map then visually communicates the magnitude of difference between the maximum and minimum values within each region.
Applications and Benefits of Peak-to-Peak Maps
Peak-to-peak maps find diverse applications across various fields, including:
- Environmental Science: Analyzing the range of temperature variations across a region, identifying areas with extreme temperature fluctuations, or visualizing the spread of pollutants.
- Economics: Depicting the range of income disparities within a country, highlighting areas with significant economic inequality, or visualizing regional variations in economic growth.
- Healthcare: Understanding the spread of disease outbreaks, identifying areas with high disease prevalence, or visualizing the range of healthcare access across a region.
- Social Sciences: Analyzing the range of social indicators like poverty, literacy, or crime rates, highlighting areas with significant social disparities, or visualizing the spread of social movements.
- Marketing and Sales: Identifying areas with high customer demand, visualizing the range of sales performance across different regions, or understanding the distribution of market share.
The benefits of utilizing peak-to-peak maps are multifaceted:
- Visual Clarity: Peak-to-peak maps offer a clear and intuitive way to understand the range of data values, making complex information readily accessible.
- Trend Identification: They facilitate the identification of areas with significant variations in data, allowing for the detection of trends and patterns.
- Spatial Analysis: Peak-to-peak maps enable the analysis of data distribution across geographical areas, providing insights into spatial patterns and relationships.
- Comparative Analysis: They allow for the comparison of data ranges across different regions or time periods, facilitating the identification of disparities and trends.
- Decision-Making Support: Peak-to-peak maps provide valuable insights that can inform decision-making processes, guiding resource allocation, policy development, and strategic planning.
Understanding the Limitations of Peak-to-Peak Maps
While powerful in their ability to visualize data ranges, peak-to-peak maps have limitations:
- Lack of Absolute Values: They do not provide information about the absolute values of data, only the range or difference between the highest and lowest values.
- Potential Distortion: The use of color gradients can sometimes distort the perception of data, particularly when dealing with large ranges.
- Data Density: Peak-to-peak maps can be less effective when dealing with highly dense data, as the visualization can become cluttered.
FAQs about Peak-to-Peak Maps
Q: What are the key elements of a peak-to-peak map?
A: Key elements include a base map, a color gradient or shading scheme representing the data range, and a legend explaining the color scale.
Q: How are peak-to-peak maps different from traditional maps?
A: Traditional maps focus on absolute values, while peak-to-peak maps emphasize the range or variation of data.
Q: What software can be used to create peak-to-peak maps?
A: Several software packages, including ArcGIS, QGIS, and Google Earth Pro, offer tools for creating peak-to-peak maps.
Q: Are peak-to-peak maps suitable for all types of data?
A: Peak-to-peak maps are most effective for data with a clear range or variation, such as temperature, income, or disease prevalence.
Q: What are some common applications of peak-to-peak maps in different fields?
A: Peak-to-peak maps are widely used in environmental science, economics, healthcare, social sciences, marketing, and sales.
Tips for Creating Effective Peak-to-Peak Maps
- Choose an appropriate color gradient: Select a color scheme that effectively communicates the range of data values, ensuring clarity and visual appeal.
- Use a clear legend: Provide a legend that explains the color scale and the corresponding data range.
- Consider the map scale: Choose a map scale that provides sufficient detail without overwhelming the viewer.
- Minimize clutter: Avoid overcrowding the map with too much information, ensuring readability and visual impact.
- Use appropriate labels: Include clear and concise labels for geographic features and data points.
Conclusion
Peak-to-peak maps serve as valuable tools for data visualization and analysis, providing a compelling visual narrative of data ranges. By highlighting the highs and lows within a dataset, these maps offer insights into trends, patterns, and disparities, supporting informed decision-making across various fields. Understanding the nuances of peak-to-peak maps, their applications, and limitations allows for the effective utilization of this powerful visualization technique for data exploration and interpretation.


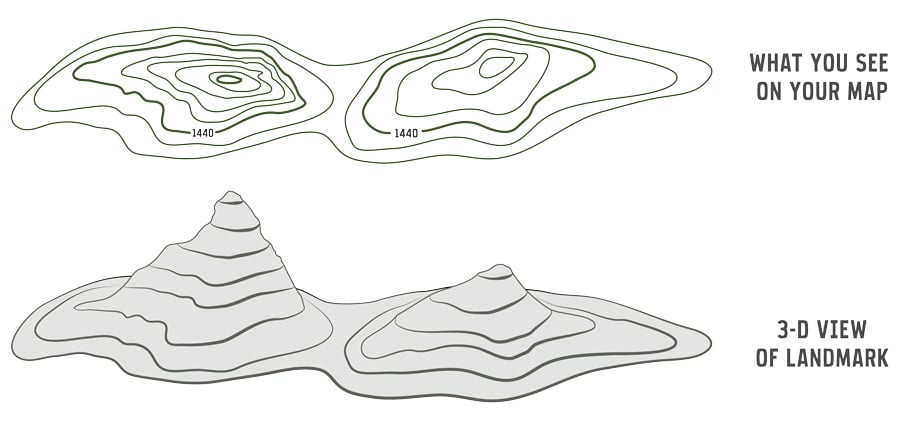


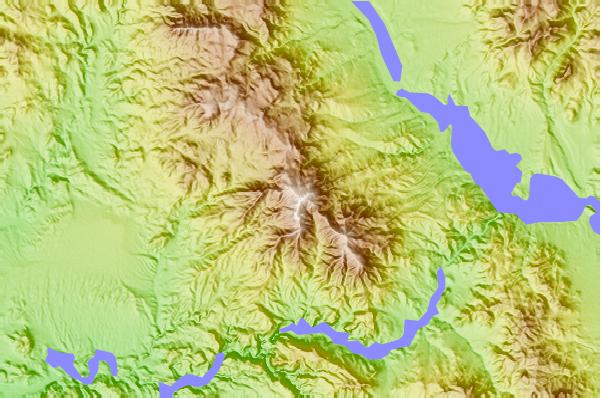

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Peaks: Understanding and Utilizing Peak-to-Peak Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To South Dakota Plat Maps
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Malaysia: A Geographical Exploration
- Navigating The World Of Digital Maps: A Comprehensive Guide To Purchasing Maps Online
- Unlocking The Secrets Of Malvern, Arkansas: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Map
- Uncovering The Treasures Of Southern Nevada: A Comprehensive Guide To The Caliente Map
- Unraveling The Topography Of Mexico: A Comprehensive Look At The Relief Map
- Navigating The Heart Of History: A Comprehensive Guide To The Athens City Map
- Navigating The Beauty Of Greece: A Guide To Printable Maps
Leave a Reply