Understanding The Political Landscape Of Iraq: A Comprehensive Guide To Its Map
Understanding the Political Landscape of Iraq: A Comprehensive Guide to its Map
Related Articles: Understanding the Political Landscape of Iraq: A Comprehensive Guide to its Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Political Landscape of Iraq: A Comprehensive Guide to its Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Political Landscape of Iraq: A Comprehensive Guide to its Map
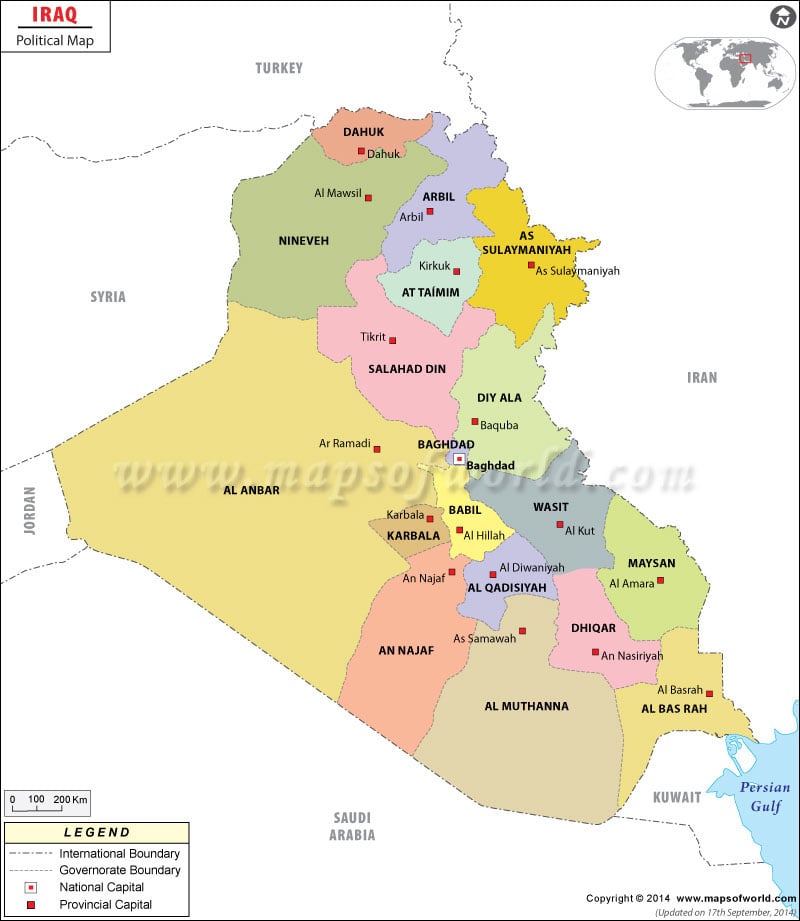
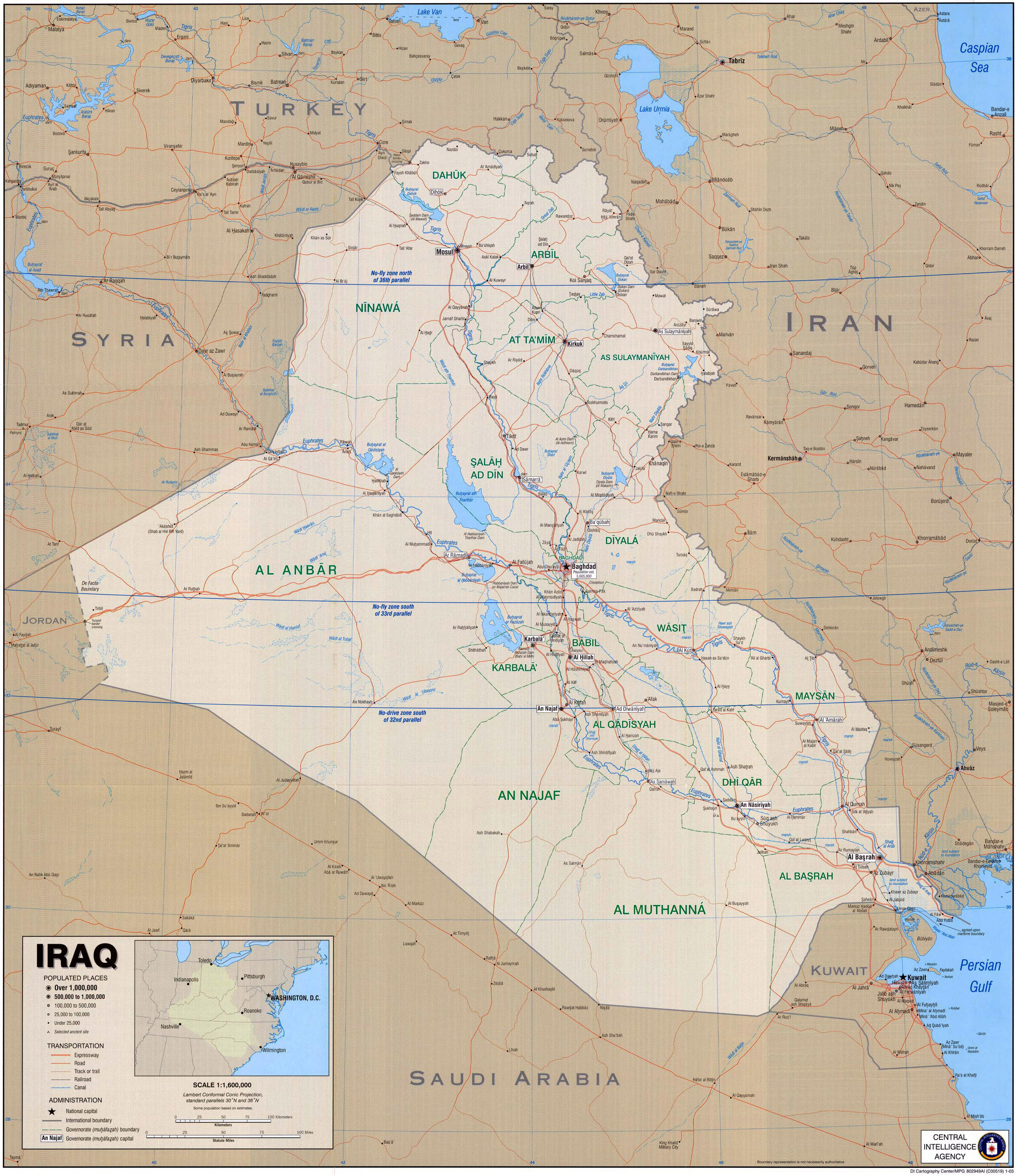
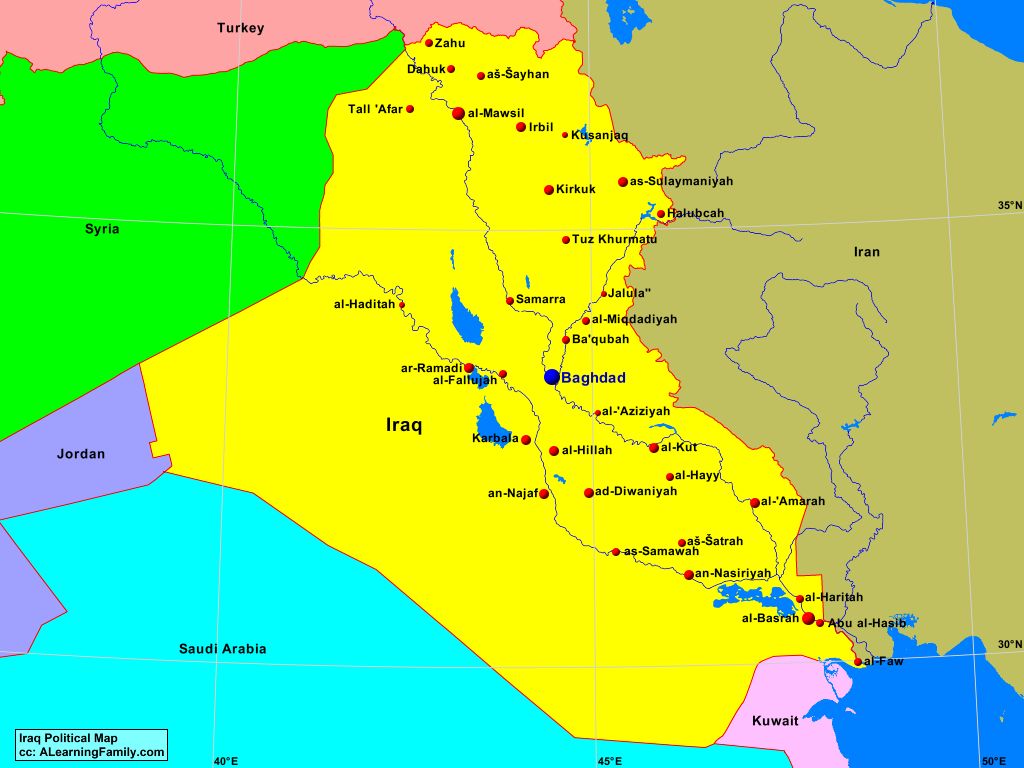
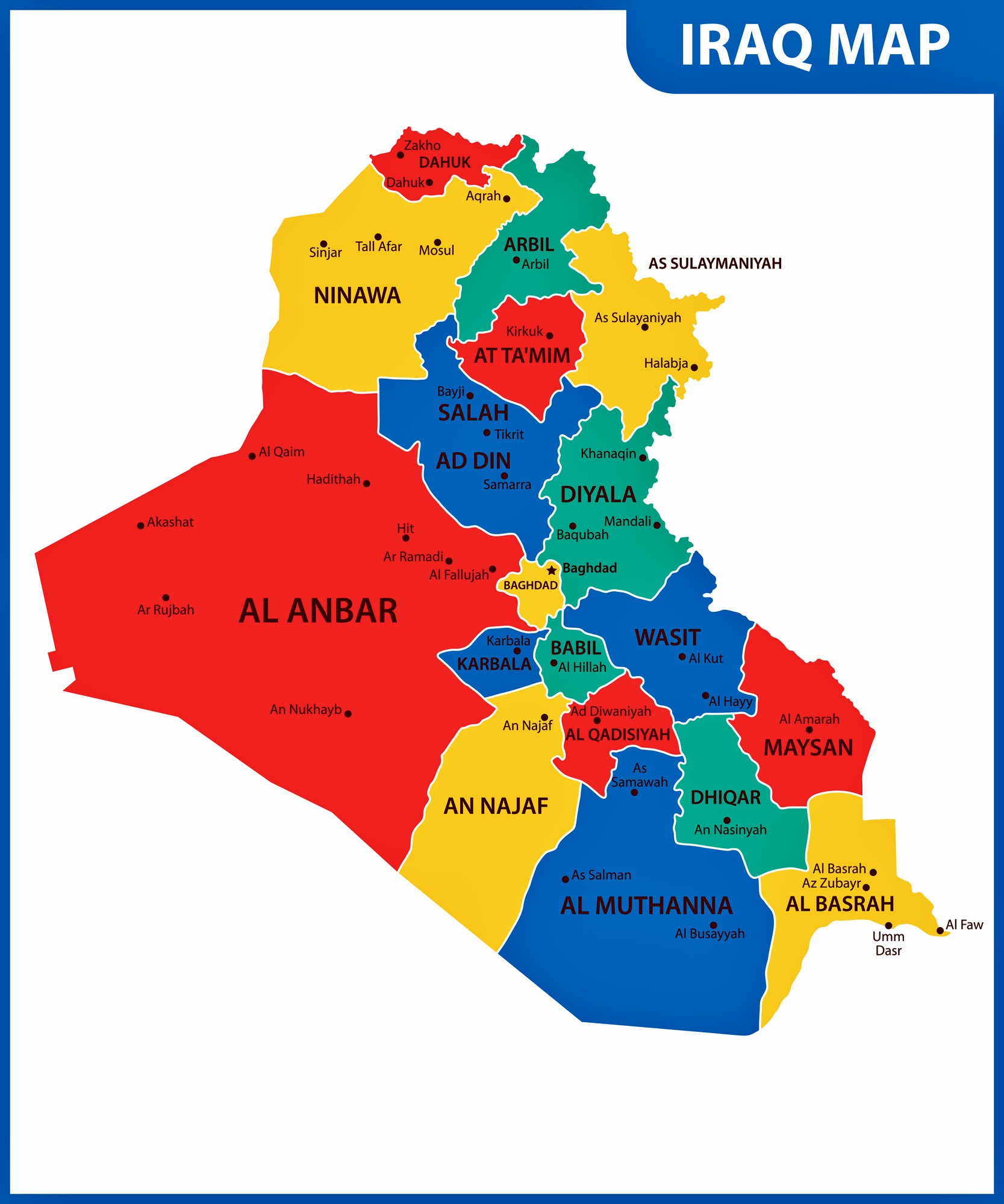
The political map of Iraq, like its history, is a complex tapestry woven from diverse ethnicities, religious groups, and power dynamics. Understanding its intricate composition is essential for comprehending the country’s contemporary challenges and potential pathways for stability and development. This comprehensive guide will delve into the key elements of Iraq’s political map, exploring its historical context, present-day divisions, and the factors shaping its future.
A Historical Overview: From Mandate to Conflict
The modern political map of Iraq emerged from the ashes of the Ottoman Empire following World War I. The League of Nations granted Britain a mandate over Mesopotamia, a region encompassing present-day Iraq, in 1920. This period saw the rise of Iraqi nationalism and the emergence of political parties advocating for independence. The Kingdom of Iraq was established in 1932, marking the end of British rule.
However, the newly formed state struggled with internal divisions and political instability. The 1958 revolution led to the overthrow of the monarchy and the establishment of a republic. Despite efforts to foster national unity, ethnic and sectarian tensions continued to simmer beneath the surface.
The Ba’athist Party’s rise to power in 1968 ushered in a period of authoritarian rule under Saddam Hussein. While the regime successfully unified the country under its control, it also implemented policies that exacerbated sectarian tensions and marginalized certain groups. This ultimately contributed to the outbreak of the Iran-Iraq War (1980-1988), which further destabilized the region and left a lasting legacy of political and social divisions.
The Post-Invasion Era: A Fragmented Landscape
The 2003 US-led invasion of Iraq marked a significant turning point in the country’s political landscape. The overthrow of Saddam Hussein’s regime led to the dissolution of the Ba’athist Party and the establishment of a new political order based on a federal system.
The 2005 constitution, drafted by the Iraqi Governing Council, enshrined the country’s multi-ethnic and multi-sectarian nature. It established a parliamentary democracy with a president, a prime minister, and a bicameral legislature. The constitution also granted significant autonomy to the Kurdish Regional Government (KRG) in northern Iraq, reflecting the long-standing aspirations of the Kurdish population for self-determination.
However, the post-invasion period witnessed a resurgence of sectarian violence and the rise of various armed groups, including al-Qaeda in Iraq and later the Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS). The power vacuum created by the collapse of Saddam Hussein’s regime allowed these groups to exploit existing ethnic and sectarian divisions, further fragmenting the political landscape.
Key Geographic Divisions: A Complex Mosaic of Identities
The political map of Iraq is characterized by a complex interplay of ethnicities, religious groups, and regional identities. While the country is officially defined as a unified entity, it is internally divided along these lines, influencing political dynamics and shaping the country’s future.
1. Ethnic Groups:
- Kurds: Comprising approximately 15-20% of the population, Kurds are concentrated in the northern region of Iraq, where they have established a semi-autonomous government. They have long sought independence from Iraq, leading to ongoing tensions and disputes with the central government.
- Arabs: The largest ethnic group in Iraq, comprising around 75-80% of the population. They are further divided along sectarian lines, with Shia Arabs dominating the south and Sunni Arabs concentrated in the center and west.
- Turkmen: A Turkic-speaking group mainly residing in the north and west of Iraq. Their political influence is generally weaker compared to Kurds and Arabs, but they play a significant role in certain regions.
- Other Minorities: Iraq is also home to smaller ethnic groups such as Assyrians, Chaldeans, Armenians, and Yazidis. These groups often face discrimination and have limited political representation.
2. Religious Groups:
- Shia Muslims: The majority religious group in Iraq, comprising around 60-65% of the population. Shia Arabs dominate the south and are politically influential, holding key positions in the government.
- Sunni Muslims: Representing around 35-40% of the population, Sunni Arabs are concentrated in the center and west of the country. They have historically held a dominant position in politics, but their influence has diminished since the 2003 invasion.
- Other Religious Groups: Iraq also has a small Christian population, primarily concentrated in the north. There are also small communities of Yazidis and other religious minorities.
3. Regional Divisions:
- Kurdistan Region: The semi-autonomous Kurdish region in northern Iraq enjoys significant political and economic autonomy. It has its own parliament, government, and military forces.
- Southern Iraq: Predominantly Shia Arab, this region is characterized by its oil wealth and its close ties to Iran. It has played a pivotal role in Iraqi politics, particularly since the 2003 invasion.
- Central Iraq: Home to Baghdad, the capital, this region is a mix of Sunni and Shia Arabs. It has been a focal point of sectarian violence and political instability.
- Western Iraq: Largely dominated by Sunni Arabs, this region has been a stronghold of anti-government forces and has witnessed significant unrest.
Challenges and Opportunities: Navigating a Complex Political Landscape
The political map of Iraq remains a work in progress, shaped by a complex interplay of ethnic, sectarian, and regional dynamics. The country faces significant challenges in navigating these divisions and achieving lasting stability.
1. Political Fragmentation: The current political system, based on a power-sharing arrangement, has been criticized for its inefficiency and for failing to adequately address the concerns of all groups. The lack of consensus among political factions often leads to political deadlock and hinders progress on crucial issues.
2. Sectarian Tensions: While the 2005 constitution attempted to reconcile sectarian differences, deep-seated divisions remain. The resurgence of sectarian violence in recent years highlights the fragility of the country’s political fabric.
3. Economic Challenges: Iraq faces significant economic challenges, including high unemployment, corruption, and a reliance on oil revenues. Addressing these issues is crucial for achieving long-term stability and development.
4. Regional Conflicts: The political map of Iraq is also influenced by regional conflicts, particularly the ongoing struggle between Iran and Saudi Arabia for influence in the country. The presence of foreign actors further complicates the political landscape.
Despite these challenges, there are also opportunities for Iraq to overcome its divisions and build a more stable and prosperous future.
1. Promoting National Reconciliation: Fostering dialogue and understanding between different ethnic and religious groups is crucial for achieving national unity. This can be achieved through inclusive political processes, economic development, and education initiatives aimed at promoting tolerance and respect for diversity.
2. Strengthening Institutions: Building strong and independent institutions, including the judiciary, the military, and civil society organizations, is essential for good governance and accountability.
3. Diversifying the Economy: Reducing reliance on oil revenues and diversifying the economy will create new opportunities for employment and growth, reducing poverty and inequality.
4. Addressing Regional Conflicts: Engaging in dialogue and diplomacy with neighboring countries to resolve regional disputes will help to create a more stable environment for Iraq.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about the Political Map of Iraq
1. What are the main ethnic groups in Iraq?
The main ethnic groups in Iraq are Kurds, Arabs, Turkmen, and various other minorities.
2. What is the significance of the Kurdish Regional Government (KRG)?
The KRG is a semi-autonomous region in northern Iraq, enjoying significant political and economic autonomy. It has its own parliament, government, and military forces. The KRG’s status and its relationship with the central government remain a source of tension.
3. What is the role of religion in Iraqi politics?
Religion plays a significant role in Iraqi politics, with both Shia and Sunni Muslims vying for influence. Sectarian divisions have been a major source of conflict in the country.
4. What are the challenges facing Iraq’s political system?
Iraq’s political system faces numerous challenges, including political fragmentation, sectarian tensions, economic difficulties, and regional conflicts.
5. What are the prospects for stability and development in Iraq?
The prospects for stability and development in Iraq remain uncertain. The country’s future will depend on its ability to address the challenges it faces and to build a more inclusive and equitable society.
Tips for Understanding the Political Map of Iraq
- Consult reputable sources: Stay informed by accessing reliable news outlets, academic journals, and think tank reports.
- Analyze historical context: Understand the historical factors that have shaped Iraq’s political map.
- Recognize the complexities: Acknowledge the intricate interplay of ethnic, sectarian, and regional dynamics.
- Engage with diverse perspectives: Seek out different viewpoints and perspectives on the political landscape.
- Follow developments closely: Stay updated on current events and political developments in Iraq.
Conclusion: A Complex Landscape with Potential for Progress
The political map of Iraq is a complex and dynamic landscape, shaped by historical legacies, ethnic and sectarian divisions, and regional conflicts. While the country faces significant challenges in navigating these complexities, it also has the potential to overcome its divisions and build a more stable and prosperous future. Understanding the intricate dynamics of Iraq’s political map is crucial for comprehending the country’s present and its potential pathways for progress. By promoting national reconciliation, strengthening institutions, diversifying the economy, and addressing regional conflicts, Iraq can work towards a brighter future for all its citizens.
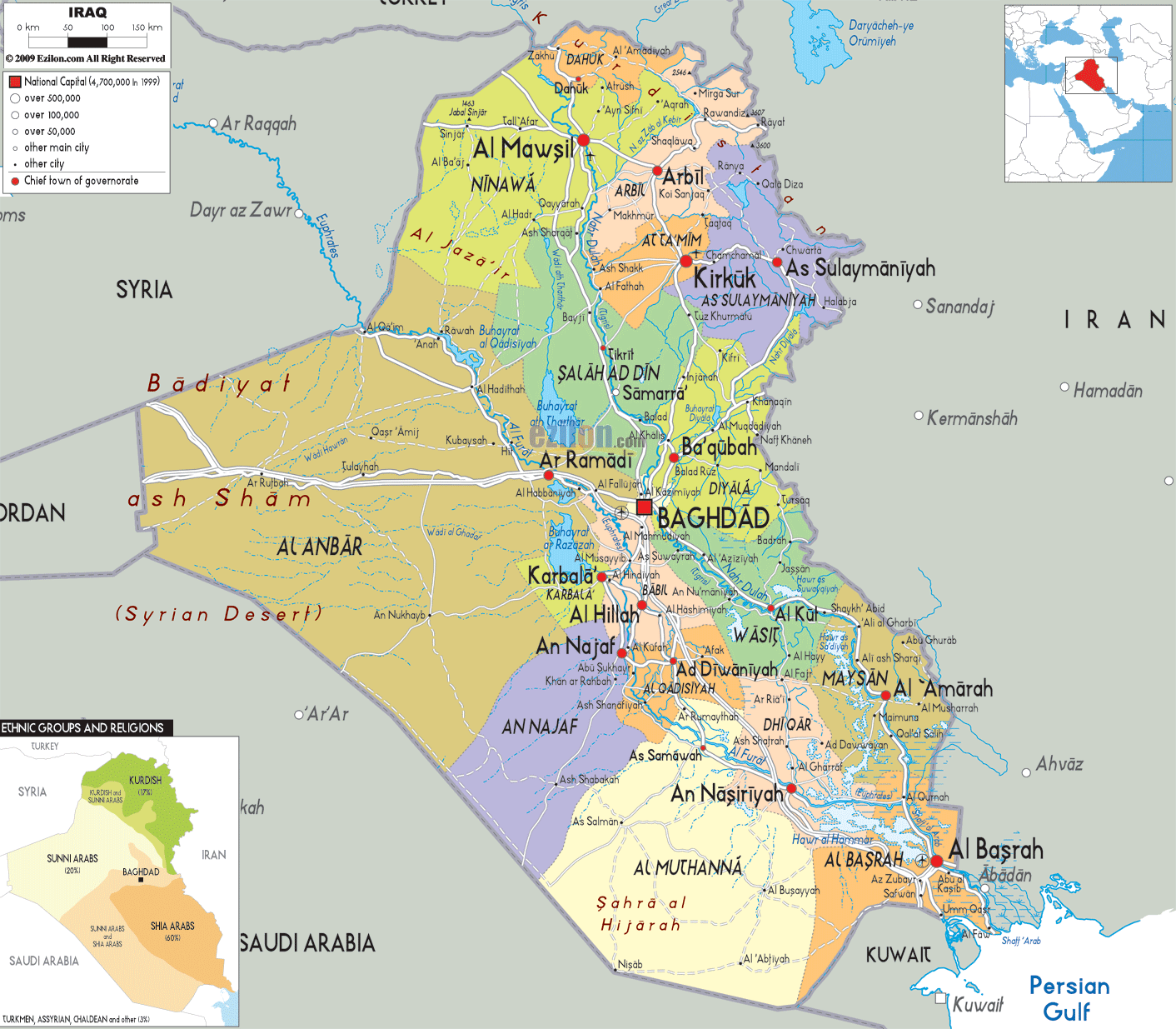


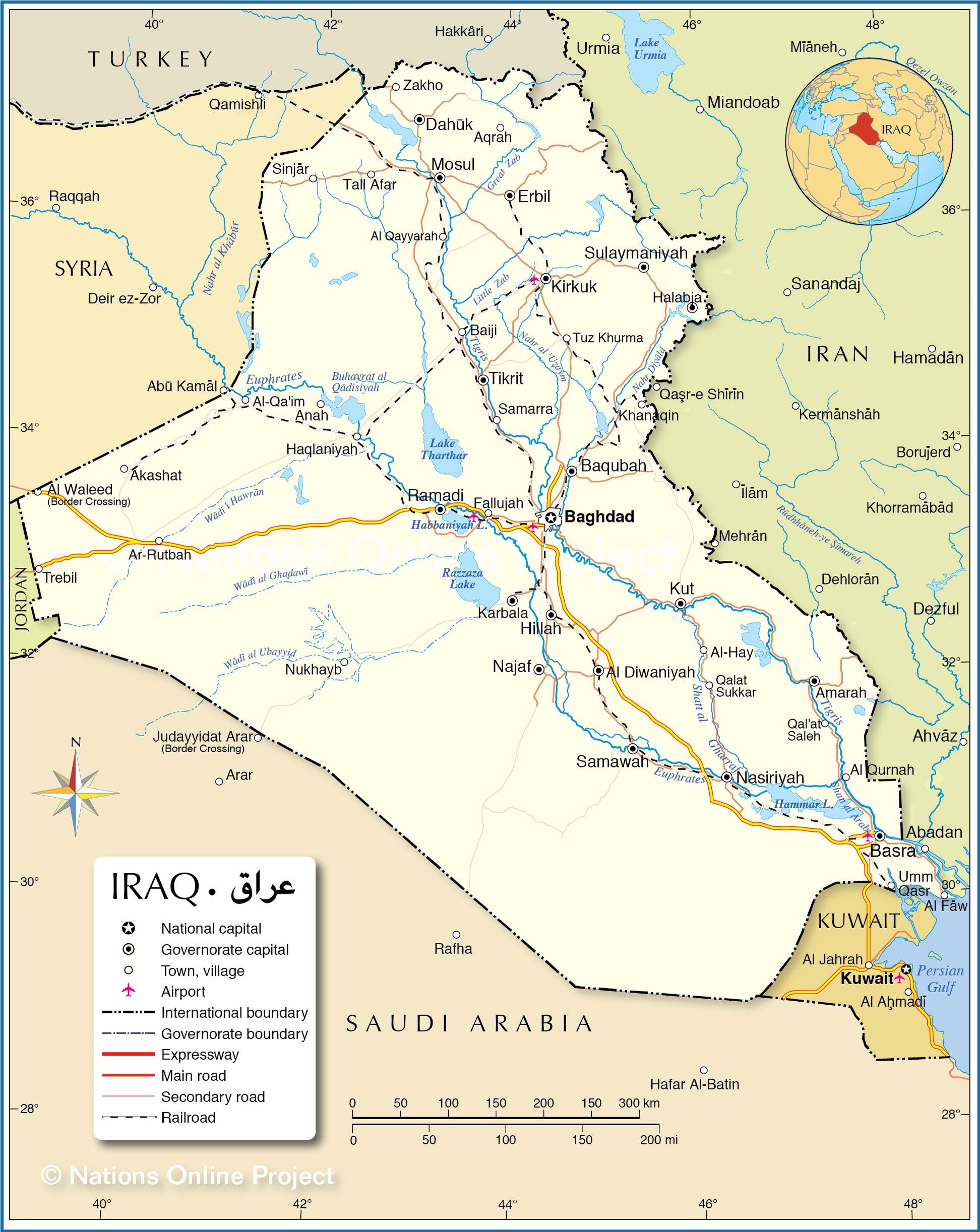
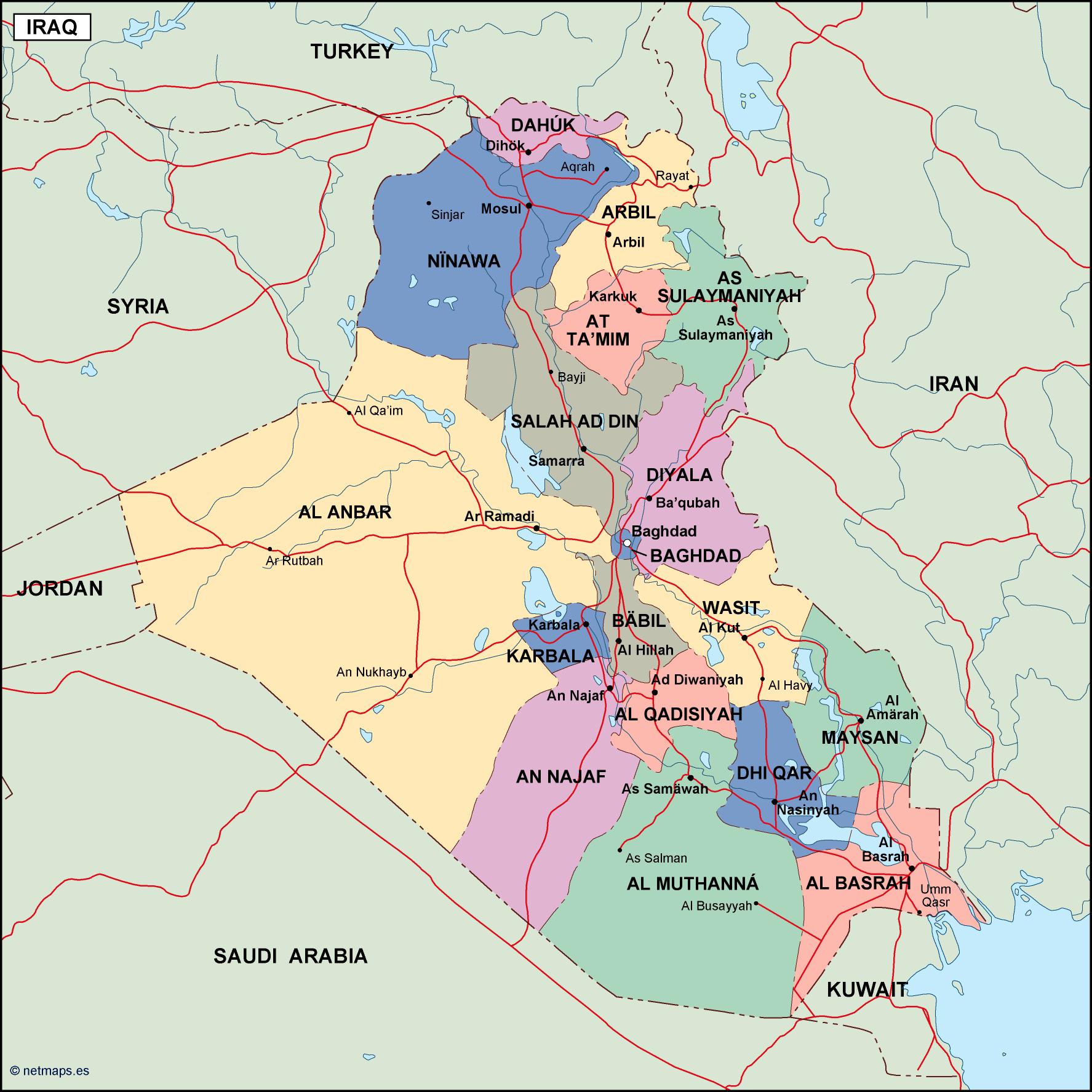
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Political Landscape of Iraq: A Comprehensive Guide to its Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To South Dakota Plat Maps
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Malaysia: A Geographical Exploration
- Navigating The World Of Digital Maps: A Comprehensive Guide To Purchasing Maps Online
- Unlocking The Secrets Of Malvern, Arkansas: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Map
- Uncovering The Treasures Of Southern Nevada: A Comprehensive Guide To The Caliente Map
- Unraveling The Topography Of Mexico: A Comprehensive Look At The Relief Map
- Navigating The Heart Of History: A Comprehensive Guide To The Athens City Map
- Navigating The Beauty Of Greece: A Guide To Printable Maps
Leave a Reply