Unraveling The Tapestry Of The Inca Empire: A Geographical Exploration
Unraveling the Tapestry of the Inca Empire: A Geographical Exploration
Related Articles: Unraveling the Tapestry of the Inca Empire: A Geographical Exploration
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Tapestry of the Inca Empire: A Geographical Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Tapestry of the Inca Empire: A Geographical Exploration

The Inca Empire, a civilization that rose to prominence in the Andes Mountains of South America, remains a captivating subject for historians and travelers alike. Its vastness, intricate social structure, and architectural marvels continue to inspire awe and wonder. Understanding the geographical footprint of this empire is crucial to appreciating its cultural significance and enduring legacy.
A Realm of Mountains and Valleys:
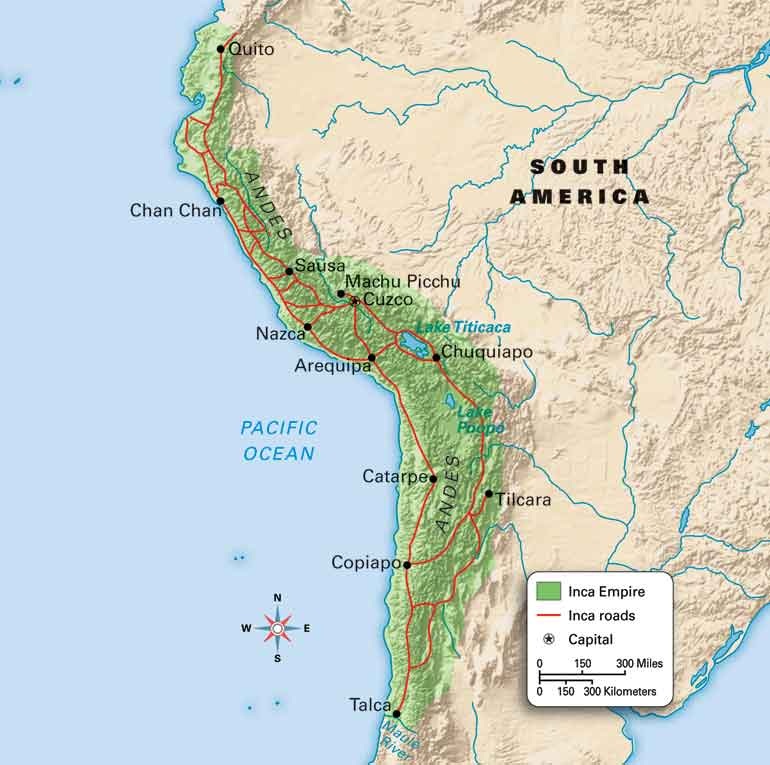
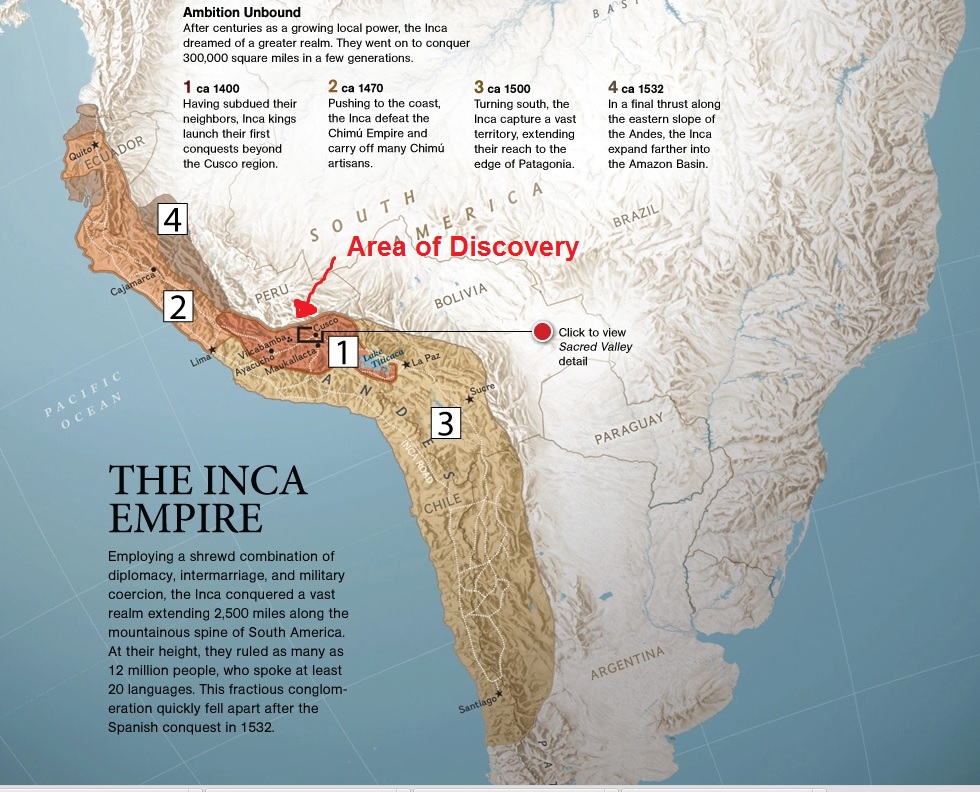
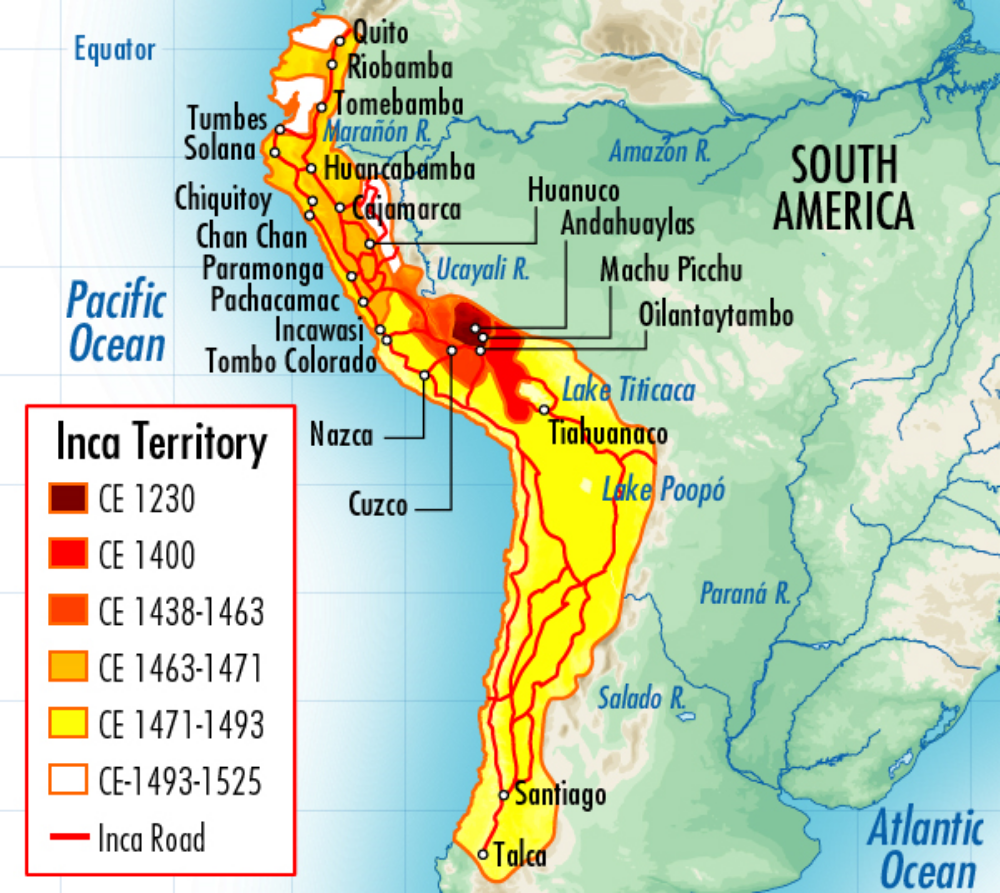
The Inca Empire, at its zenith, stretched across a sprawling territory encompassing parts of modern-day Peru, Bolivia, Ecuador, Chile, and Argentina. Its heartland, however, lay nestled within the Andean highlands, a region characterized by towering mountains, fertile valleys, and diverse ecological zones.
The Andean Backbone:
The Andes Mountains, a formidable geological formation, served as the defining feature of the Inca landscape. The empire’s dominion extended along the western slopes of the Andes, with its major cities and administrative centers strategically positioned within the valleys and plateaus.
From Coastal Deserts to Jungle Rainforests:
The Inca Empire’s geographical reach was remarkable. It extended westward to the arid coastal deserts of the Pacific Ocean, where fishing and agriculture flourished. To the east, the empire embraced the lush rainforests of the Amazon basin, a region teeming with diverse flora and fauna.
A Network of Roads:
The Inca Empire was renowned for its extensive road system, known as the Qhapaq Ñan. This network of paved pathways, spanning over 40,000 kilometers, connected the empire’s far-flung regions, facilitating communication, trade, and military movements.
Key Cities and Administrative Centers:
The Inca Empire was not a monolithic entity but rather a complex tapestry of interconnected cities and administrative centers. Each region within the empire had its own distinct characteristics and cultural nuances.
Cuzco: The Heart of the Empire:
Cuzco, located in the heart of the Andean highlands, served as the Inca capital. Its strategic location, nestled amidst fertile valleys and surrounded by towering mountains, made it an ideal hub for political, religious, and economic activity.
Machu Picchu: The Lost City of the Incas:
Machu Picchu, perched high in the Andes Mountains, is perhaps the most iconic symbol of the Inca Empire. This enigmatic city, shrouded in mystery for centuries, is a testament to the architectural ingenuity and engineering prowess of the Incas.
Other Notable Cities:
Other significant Inca cities included:
- Sacsayhuamán: A massive fortress located near Cuzco, showcasing the Incas’ mastery of stonework.
- Ollantaytambo: A town in the Sacred Valley, renowned for its intricate terraces and temple complexes.
- Pisac: A town known for its colorful markets and ancient ruins, including a ceremonial center.
The Legacy of the Inca Empire:
The Inca Empire, though conquered by the Spanish in the 16th century, left an indelible mark on the history and culture of South America. Its legacy is evident in the languages, traditions, and architectural marvels that continue to captivate the world.
FAQs:
1. What are the geographical boundaries of the Inca Empire?
The Inca Empire, at its peak, extended from southern Colombia to northern Chile, encompassing parts of present-day Peru, Bolivia, Ecuador, and Argentina. Its heartland, however, lay within the Andean highlands.
2. How did the Incas adapt to the diverse geography of their empire?
The Incas developed sophisticated agricultural techniques, including terracing, irrigation systems, and the cultivation of a variety of crops, to thrive in the diverse ecological zones of their empire. They also constructed extensive road systems and administrative structures to connect and manage their far-flung territories.
3. What are the key features of the Inca road system?
The Inca road system, known as the Qhapaq Ñan, was a remarkable feat of engineering. It spanned over 40,000 kilometers, connecting the empire’s major cities, administrative centers, and remote villages. The roads were paved with stones and featured bridges, tunnels, and rest stops, facilitating communication, trade, and military movements.
4. How did the geographical location of Cuzco contribute to its importance as the Inca capital?
Cuzco’s strategic location, nestled amidst fertile valleys and surrounded by towering mountains, made it an ideal hub for political, religious, and economic activity. Its accessibility to trade routes, agricultural resources, and strategic vantage points contributed to its prominence as the heart of the Inca Empire.
5. What is the significance of Machu Picchu in the context of the Inca Empire?
Machu Picchu, a lost city perched high in the Andes Mountains, is a testament to the architectural ingenuity and engineering prowess of the Incas. Its strategic location, complex architecture, and intricate water systems highlight the sophistication of Inca civilization.
Tips for Exploring the Inca Empire:
- Plan your itinerary: Research the different regions within the Inca Empire and prioritize the sites you wish to visit.
- Book accommodations in advance: Popular destinations, such as Cuzco and Machu Picchu, tend to be crowded, so it’s wise to secure accommodation well in advance.
- Hire a local guide: A knowledgeable guide can provide valuable insights into the history, culture, and significance of the Inca sites you visit.
- Pack appropriately: The Andes Mountains can be cold and unpredictable, so be sure to pack warm clothing, sturdy hiking boots, and rain gear.
- Learn basic Spanish: While English is widely spoken in tourist areas, learning a few basic Spanish phrases can enhance your interactions with locals.
Conclusion:
The Inca Empire, a civilization that flourished in the Andes Mountains, left an enduring legacy on the history and culture of South America. Its vast geographical footprint, encompassing diverse ecological zones, highlights its adaptability and resilience. From the towering peaks of the Andes to the lush rainforests of the Amazon, the Inca Empire’s presence is felt throughout the region. Its architectural marvels, intricate social structures, and sophisticated road systems continue to inspire awe and wonder, reminding us of the ingenuity and resilience of this remarkable civilization.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Tapestry of the Inca Empire: A Geographical Exploration. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To South Dakota Plat Maps
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Malaysia: A Geographical Exploration
- Navigating The World Of Digital Maps: A Comprehensive Guide To Purchasing Maps Online
- Unlocking The Secrets Of Malvern, Arkansas: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Map
- Uncovering The Treasures Of Southern Nevada: A Comprehensive Guide To The Caliente Map
- Unraveling The Topography Of Mexico: A Comprehensive Look At The Relief Map
- Navigating The Heart Of History: A Comprehensive Guide To The Athens City Map
- Navigating The Beauty Of Greece: A Guide To Printable Maps
Leave a Reply