Unveiling Earth’s Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide To World Map Land Features
Unveiling Earth’s Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to World Map Land Features
Related Articles: Unveiling Earth’s Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to World Map Land Features
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Earth’s Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to World Map Land Features. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling Earth’s Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to World Map Land Features

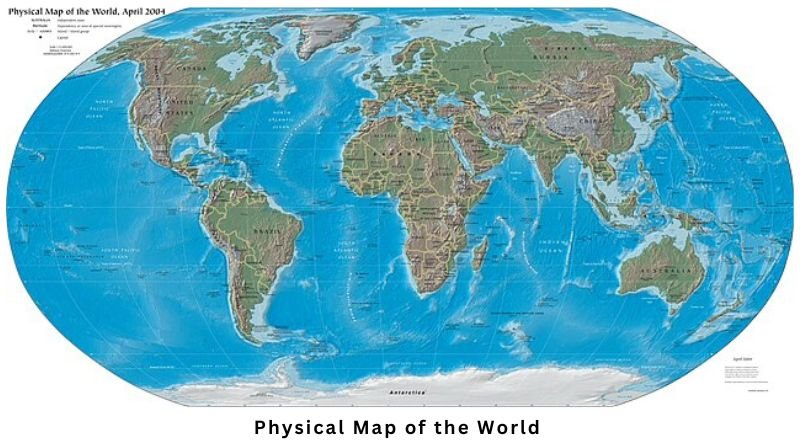
The Earth’s surface, a mesmerizing tapestry of diverse landscapes, is intricately woven with a myriad of land features. These features, ranging from towering mountains to vast plains, from fertile valleys to arid deserts, are the defining characteristics of our planet, shaping its ecosystems, influencing its climate, and impacting human civilization.
This comprehensive guide delves into the fascinating world of world map land features, exploring their formation, classification, and significance.
A Journey Through Earth’s Landforms
1. Mountains: The Earth’s Backbone
Mountains, the majestic giants of the Earth’s surface, rise dramatically above the surrounding terrain. These towering formations are the result of tectonic plate collisions, where immense pressure forces the Earth’s crust to buckle and fold, creating towering peaks.
-
Types of Mountains: Mountains are classified based on their formation:
- Fold Mountains: Formed by the folding of rock layers, often found in chains, such as the Himalayas and the Andes.
- Block Mountains: Created by the uplift of large blocks of land, separated by faults, like the Sierra Nevada in California.
- Volcanic Mountains: Formed by the accumulation of lava and ash erupted from volcanoes, such as Mount Fuji in Japan.
-
Importance of Mountains:
- Climate Regulation: Mountains influence weather patterns, creating rain shadows and shaping regional climates.
- Biodiversity Hotspots: Mountains harbor unique ecosystems and a diverse range of plant and animal species.
- Water Resources: Mountains serve as vital sources of freshwater, feeding rivers and providing drinking water for millions.
2. Plateaus: Elevated Landscapes
Plateaus, often referred to as tablelands, are elevated flat areas of land, characterized by relatively level surfaces and steep slopes. They are formed through a variety of geological processes, including volcanic activity, tectonic uplift, and erosion.
-
Formation of Plateaus:
- Volcanic Plateaus: Formed by extensive lava flows, such as the Deccan Plateau in India.
- Tectonic Plateaus: Created by the uplift of large blocks of land, like the Colorado Plateau in the United States.
- Erosion Plateaus: Formed by the erosion of surrounding mountains, leaving behind a flat, elevated surface.
-
Significance of Plateaus:
- Mineral Resources: Plateaus often contain valuable mineral deposits, such as diamonds and gold.
- Agricultural Potential: Some plateaus have fertile soils suitable for agriculture, like the Tibetan Plateau.
- Scenic Beauty: Plateaus offer breathtaking views and unique landscapes, attracting tourists and adventurers.
3. Plains: The Earth’s Expansive Canvas
Plains, vast stretches of relatively flat land, are characterized by gentle slopes and minimal elevation changes. These expansive areas are formed through a combination of erosion and deposition processes.
-
Types of Plains:
- Coastal Plains: Formed by the deposition of sediments along coastlines, often fertile and suitable for agriculture.
- Alluvial Plains: Created by the deposition of sediments by rivers, like the Great Plains of North America.
- Structural Plains: Formed by the erosion of uplifted land, such as the Great Plains of Australia.
-
Importance of Plains:
- Agriculture and Food Production: Plains are essential for agriculture, providing vast areas for farming and livestock grazing.
- Transportation and Infrastructure: Their flat terrain facilitates transportation and the construction of infrastructure.
- Human Settlement: Plains have historically been attractive locations for human settlements due to their fertile soils and accessibility.
4. Valleys: Landforms of Erosion and Deposition
Valleys, depressions in the Earth’s surface, are formed primarily through the erosion of rivers, glaciers, or tectonic activity. They are characterized by a distinct channel and slopes on either side.
-
Types of Valleys:
- River Valleys: Formed by the erosion of rivers, often with a U-shaped cross-section.
- Glacial Valleys: Created by the erosive power of glaciers, typically U-shaped and with steep sides.
- Structural Valleys: Formed by tectonic activity, such as the Rift Valley in Africa.
-
Significance of Valleys:
- Water Resources: Valleys often contain rivers and streams, providing essential water resources for human use and ecosystems.
- Agriculture and Settlement: Valleys often have fertile soils and favorable climates, making them suitable for agriculture and human settlement.
- Tourism and Recreation: Valleys offer scenic beauty, opportunities for outdoor recreation, and potential for tourism development.
5. Deserts: Arid Landscapes of Extremes
Deserts, characterized by extreme dryness and low rainfall, are found in various regions of the world. Their formation is influenced by factors like prevailing winds, mountain ranges, and ocean currents.
-
Types of Deserts:
- Hot Deserts: Located in subtropical regions, characterized by high temperatures and low humidity, such as the Sahara Desert in Africa.
- Cold Deserts: Found in high latitudes or mountainous regions, with low temperatures and limited precipitation, like the Gobi Desert in Asia.
- Coastal Deserts: Located on the western coasts of continents, influenced by cold ocean currents, such as the Atacama Desert in Chile.
-
Importance of Deserts:
- Unique Ecosystems: Deserts harbor specialized plant and animal life adapted to survive harsh conditions.
- Mineral Resources: Deserts often contain valuable mineral deposits, such as copper and iron ore.
- Tourism and Recreation: Deserts offer unique landscapes and opportunities for adventure tourism.
6. Canyons: Sculptural Wonders of Erosion
Canyons, deep gorges with steep sides, are formed by the erosive power of rivers or glaciers over long periods. These dramatic features are a testament to the relentless forces of nature.
-
Formation of Canyons:
- River Canyons: Formed by rivers carving through rock over millions of years, such as the Grand Canyon in the United States.
- Glacial Canyons: Created by the erosive power of glaciers, typically U-shaped and with steep sides.
-
Significance of Canyons:
- Geological History: Canyons expose layers of rock, providing insights into Earth’s geological history.
- Biodiversity: Canyons often harbor unique ecosystems and a diverse range of plant and animal species.
- Tourism and Recreation: Canyons attract tourists and adventurers, offering opportunities for hiking, camping, and exploring.
7. Islands: Emergent Landmasses
Islands, landmasses surrounded by water, are formed through various geological processes.
-
Types of Islands:
- Continental Islands: Formed by the separation of a landmass from a continent, like Madagascar.
- Oceanic Islands: Formed by volcanic activity or coral reef growth, such as Hawaii.
-
Importance of Islands:
- Biodiversity: Islands often harbor unique ecosystems and endemic species found nowhere else.
- Tourism and Recreation: Islands are popular destinations for tourism and recreation, offering beaches, coral reefs, and unique cultural experiences.
- Resource Potential: Islands can contain valuable resources, such as oil and gas deposits.
8. Peninsulas: Projections of Land
Peninsulas, landmasses that extend into a body of water, are characterized by a narrow neck connecting them to the mainland. They are formed by various geological processes, including tectonic activity and erosion.
-
Significance of Peninsulas:
- Strategic Location: Peninsulas often occupy strategic locations, controlling access to waterways and providing natural defenses.
- Coastal Resources: Peninsulas have extensive coastlines, providing opportunities for fishing, shipping, and tourism.
- Unique Landscapes: Peninsulas often exhibit diverse landscapes, from rugged coastlines to fertile plains.
The Importance of World Map Land Features
The diverse array of world map land features plays a crucial role in shaping our planet’s environment, ecosystems, and human civilization.
- Climate Regulation: Land features influence weather patterns, creating rain shadows, moderating temperatures, and shaping regional climates.
- Biodiversity Hotspots: Mountains, plateaus, and islands often harbor unique ecosystems and a diverse range of plant and animal species, contributing to global biodiversity.
- Water Resources: Mountains, plateaus, and valleys serve as vital sources of freshwater, feeding rivers and providing drinking water for millions.
- Resource Potential: Land features often contain valuable mineral deposits, oil and gas reserves, and fertile soils for agriculture.
- Human Settlement and Development: Plains, valleys, and coastal regions have historically been attractive locations for human settlements due to their fertile soils, accessibility, and resources.
FAQs about World Map Land Features
Q1. How are mountains formed?
A1. Mountains are primarily formed by the collision of tectonic plates, where immense pressure forces the Earth’s crust to buckle and fold, creating towering peaks.
Q2. What is the difference between a plateau and a plain?
A2. Plateaus are elevated flat areas of land with steep slopes, while plains are vast stretches of relatively flat land with gentle slopes and minimal elevation changes.
Q3. How are deserts formed?
A3. Deserts are formed by a combination of factors, including prevailing winds, mountain ranges, and ocean currents, which create dry conditions with low rainfall.
Q4. What is the significance of islands?
A4. Islands are important for their unique ecosystems, endemic species, tourism potential, and potential resource reserves.
Q5. How are peninsulas formed?
A5. Peninsulas are formed by various geological processes, including tectonic activity and erosion, which create landmasses that extend into a body of water.
Tips for Understanding World Map Land Features
- Use a globe or map: A visual representation of the Earth’s surface provides a better understanding of the location and distribution of land features.
- Explore online resources: Many websites and educational platforms offer detailed information and interactive maps of world map land features.
- Travel and observe: Visiting different regions of the world allows for firsthand observation and appreciation of the diverse land features.
- Read books and documentaries: There are numerous books and documentaries that delve into the formation, significance, and impact of world map land features.
Conclusion
The Earth’s surface, a captivating tapestry of diverse landscapes, is defined by a myriad of land features. From towering mountains to vast plains, from fertile valleys to arid deserts, these formations shape our planet’s environment, ecosystems, and human civilization. Understanding the formation, classification, and significance of world map land features provides a deeper appreciation for the intricate workings of our planet and the crucial role they play in sustaining life. By studying and appreciating these features, we can better understand the interconnectedness of our world and the importance of preserving its natural wonders for future generations.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Earth’s Tapestry: A Comprehensive Guide to World Map Land Features. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To South Dakota Plat Maps
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Malaysia: A Geographical Exploration
- Navigating The World Of Digital Maps: A Comprehensive Guide To Purchasing Maps Online
- Unlocking The Secrets Of Malvern, Arkansas: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Map
- Uncovering The Treasures Of Southern Nevada: A Comprehensive Guide To The Caliente Map
- Unraveling The Topography Of Mexico: A Comprehensive Look At The Relief Map
- Navigating The Heart Of History: A Comprehensive Guide To The Athens City Map
- Navigating The Beauty Of Greece: A Guide To Printable Maps
Leave a Reply