Unveiling The Power Of The Wind: A Comprehensive Guide To Annual Average Wind Speed Maps
Unveiling the Power of the Wind: A Comprehensive Guide to Annual Average Wind Speed Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of the Wind: A Comprehensive Guide to Annual Average Wind Speed Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of the Wind: A Comprehensive Guide to Annual Average Wind Speed Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of the Wind: A Comprehensive Guide to Annual Average Wind Speed Maps
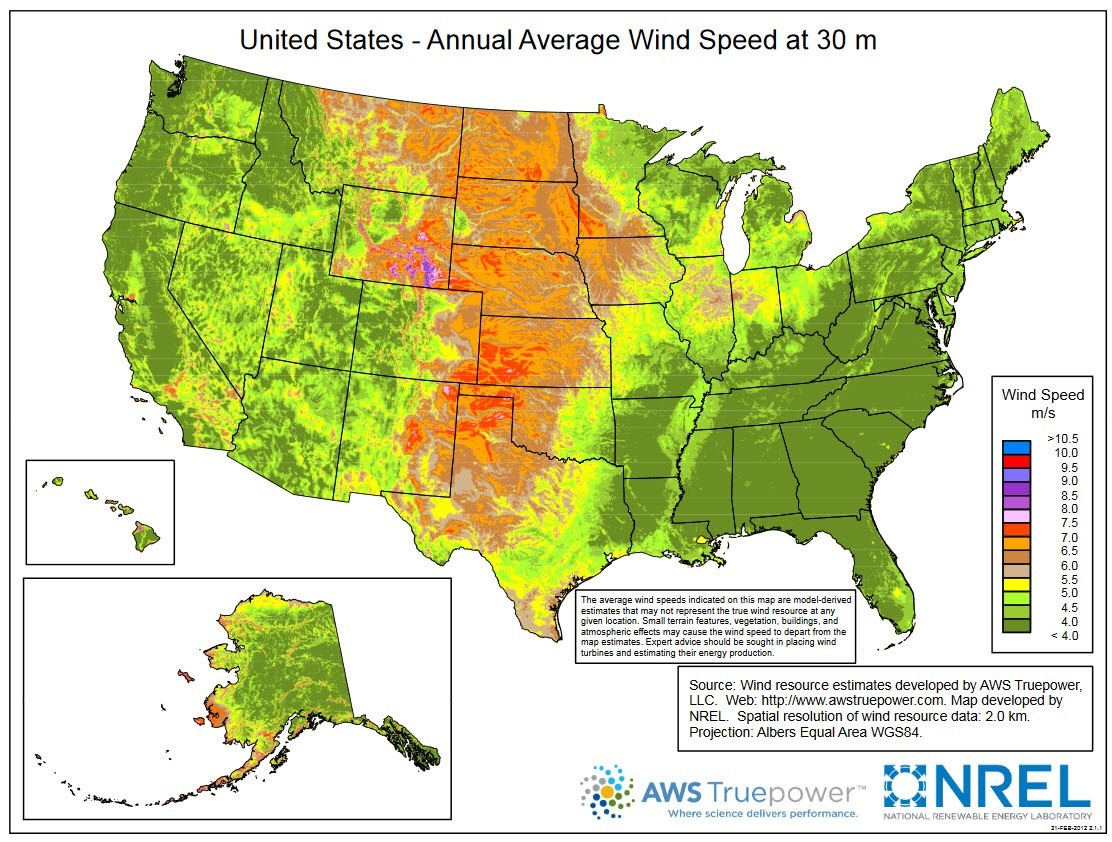
The Earth’s atmosphere is in constant motion, driven by a complex interplay of factors like solar radiation, the Earth’s rotation, and geographical features. This dynamic movement manifests in various forms, including winds, which play a crucial role in shaping our planet’s climate and influencing numerous aspects of human life. Understanding the patterns and strength of these winds is essential for diverse applications, from weather forecasting to renewable energy generation.
Visualizing Wind Power: The Significance of Annual Average Wind Speed Maps
Annual average wind speed maps serve as powerful tools for visualizing and understanding the global distribution of wind energy potential. These maps depict the average wind speed at various locations across the globe over a year, providing valuable insights into wind resource availability. They are instrumental in:
- Renewable Energy Development: Wind speed maps are crucial for identifying areas with high wind potential, guiding the selection of optimal locations for wind turbine installations. This information is essential for maximizing energy generation and ensuring the economic viability of wind energy projects.
- Weather Forecasting: Understanding wind patterns is fundamental for accurate weather forecasting. Maps depicting average wind speeds provide a baseline for predicting wind direction and strength, enabling meteorologists to develop more precise forecasts.
- Climate Research: Wind patterns are intricately linked to global climate systems. Annual average wind speed maps help scientists understand the dynamics of atmospheric circulation, analyze climate change impacts, and develop models to predict future climate scenarios.
- Aviation and Maritime Navigation: Wind speed and direction are crucial for safe and efficient air and sea travel. Pilots and mariners rely on wind data to optimize flight paths and sailing routes, minimizing fuel consumption and travel time.
- Environmental Studies: Wind patterns influence various environmental processes, including the dispersal of pollutants, seed dispersal, and the movement of sand dunes. Wind speed maps provide valuable data for understanding these processes and developing strategies for environmental management.
Decoding the Map: Understanding the Data and Its Interpretation
Annual average wind speed maps typically display wind speed data in units of meters per second (m/s) or kilometers per hour (km/h). They often use a color gradient to represent different wind speed ranges, with darker shades indicating higher wind speeds.
Interpreting these maps requires understanding the factors that influence wind speed:
- Geographical Location: Wind patterns are influenced by geographic features like mountains, valleys, and coastlines. Mountains can create wind funneling effects, increasing wind speeds in certain areas, while valleys can act as wind barriers, reducing wind speeds. Coastal areas often experience stronger winds due to the interaction between land and sea.
- Altitude: Wind speeds generally increase with altitude due to reduced friction with the Earth’s surface. This is why wind turbines are typically placed on high ground or towers to maximize energy generation.
- Seasonal Variations: Wind patterns can vary significantly throughout the year due to seasonal changes in temperature, pressure gradients, and atmospheric circulation patterns. Annual average wind speed maps provide a general overview of wind potential, but it’s important to consider seasonal variations for specific applications.
Exploring the World’s Wind Resources: Case Studies and Examples
- The United States: The central and northern plains states, particularly in the Great Plains region, are renowned for their strong and consistent winds, making them prime locations for wind energy development.
- Europe: Countries like Denmark, Germany, and Spain have heavily invested in wind energy, leveraging their abundant wind resources to generate a significant portion of their electricity.
- China: With a vast landmass and diverse terrain, China has a wide range of wind resources. The northern and eastern regions are particularly windy, supporting a growing wind energy industry.
- Australia: Australia boasts vast open spaces and strong winds, particularly in the coastal areas and the southern and western regions, making it a global leader in wind energy.
Beyond the Average: Unveiling the Importance of Wind Variability
While annual average wind speed maps offer a valuable snapshot of wind potential, it’s crucial to recognize the importance of wind variability. Wind speed can fluctuate significantly over time due to:
- Diurnal Variations: Wind speeds often vary throughout the day, typically reaching peak levels during the afternoon and evening hours.
- Weather Events: Storms, fronts, and other weather events can cause sudden and dramatic shifts in wind speed and direction.
- Topographical Effects: Wind patterns can be significantly influenced by local terrain features, leading to localized variations in wind speed.
Understanding these variations is critical for:
- Optimizing Wind Turbine Performance: Wind turbines are designed to operate efficiently within a specific range of wind speeds. Understanding wind variability allows for the selection of turbines that are well-suited to the specific location and for optimizing their operation to maximize energy generation.
- Ensuring Grid Stability: Fluctuations in wind speed can impact the stability of the electricity grid. By understanding and predicting these variations, energy companies can develop strategies to mitigate potential disruptions and ensure a reliable energy supply.
- Improving Weather Forecasting: Incorporating data on wind variability into weather models can improve the accuracy of forecasts, leading to better preparedness for extreme weather events.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Annual Average Wind Speed Maps
Q: What are the units used to measure wind speed on these maps?
A: Wind speed on these maps is typically measured in meters per second (m/s) or kilometers per hour (km/h).
Q: How is the average wind speed calculated for a specific location?
A: The average wind speed is calculated by taking the average of wind speed measurements collected over a year at that location.
Q: Are these maps reliable for predicting future wind conditions?
A: While these maps provide a general overview of wind potential, they don’t necessarily guarantee future wind conditions. Wind speed can fluctuate significantly due to various factors, including weather events and seasonal variations.
Q: What are the limitations of these maps?
A: These maps represent annual averages, so they don’t capture the full range of wind variability. They also don’t account for local topographical effects, which can significantly influence wind patterns.
Q: How can I find wind speed data for a specific location?
A: You can find wind speed data for specific locations from various sources, including government agencies like the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) in the United States, meteorological services in other countries, and private weather data providers.
Tips for Using Annual Average Wind Speed Maps
- Consider the scale of the map: Maps at different scales may provide different levels of detail. For local applications, it’s essential to use maps with a high level of detail.
- Pay attention to the color scale: The color scale used on the map indicates the range of wind speeds. Ensure you understand the meaning of different colors before interpreting the data.
- Factor in wind variability: Remember that annual average wind speed maps only represent average conditions. Consider the potential for wind variability when making decisions based on the data.
- Consult additional resources: Supplement your analysis with data from other sources, such as historical wind speed records, weather forecasts, and local meteorological information.
Conclusion: The Power of Wind Data for a Sustainable Future
Annual average wind speed maps are valuable tools for understanding the global distribution of wind energy potential and for supporting diverse applications ranging from renewable energy development to weather forecasting and climate research. They provide a crucial starting point for exploring wind resources, but it’s important to remember that they only represent average conditions. By considering wind variability, local topographical effects, and other relevant factors, we can harness the power of wind data to make informed decisions and build a more sustainable future.
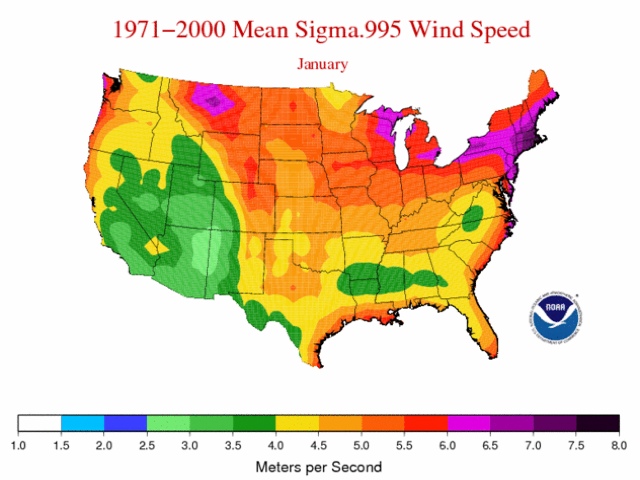
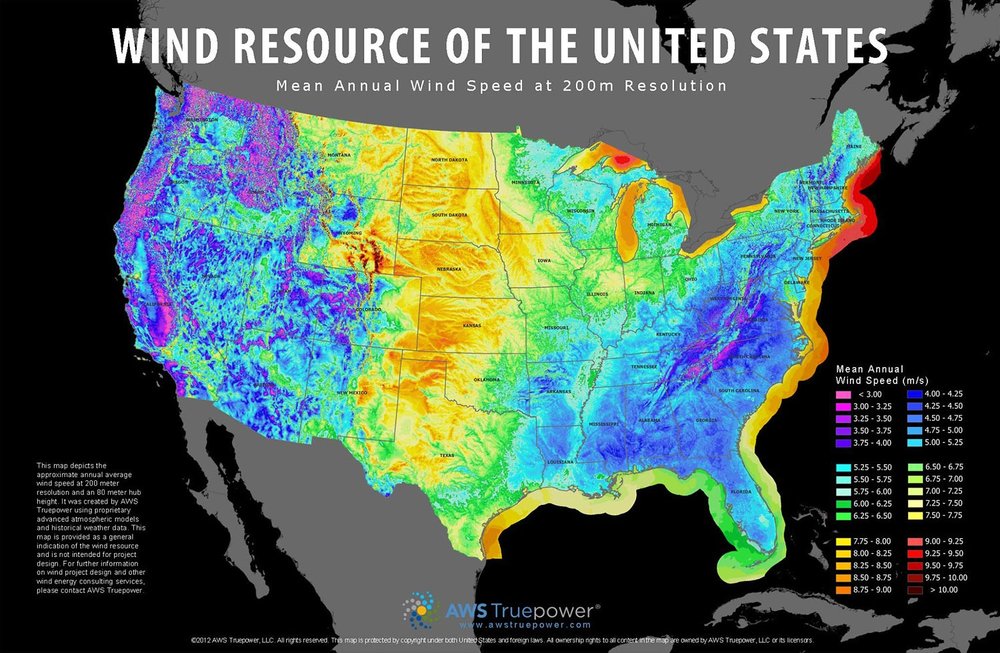
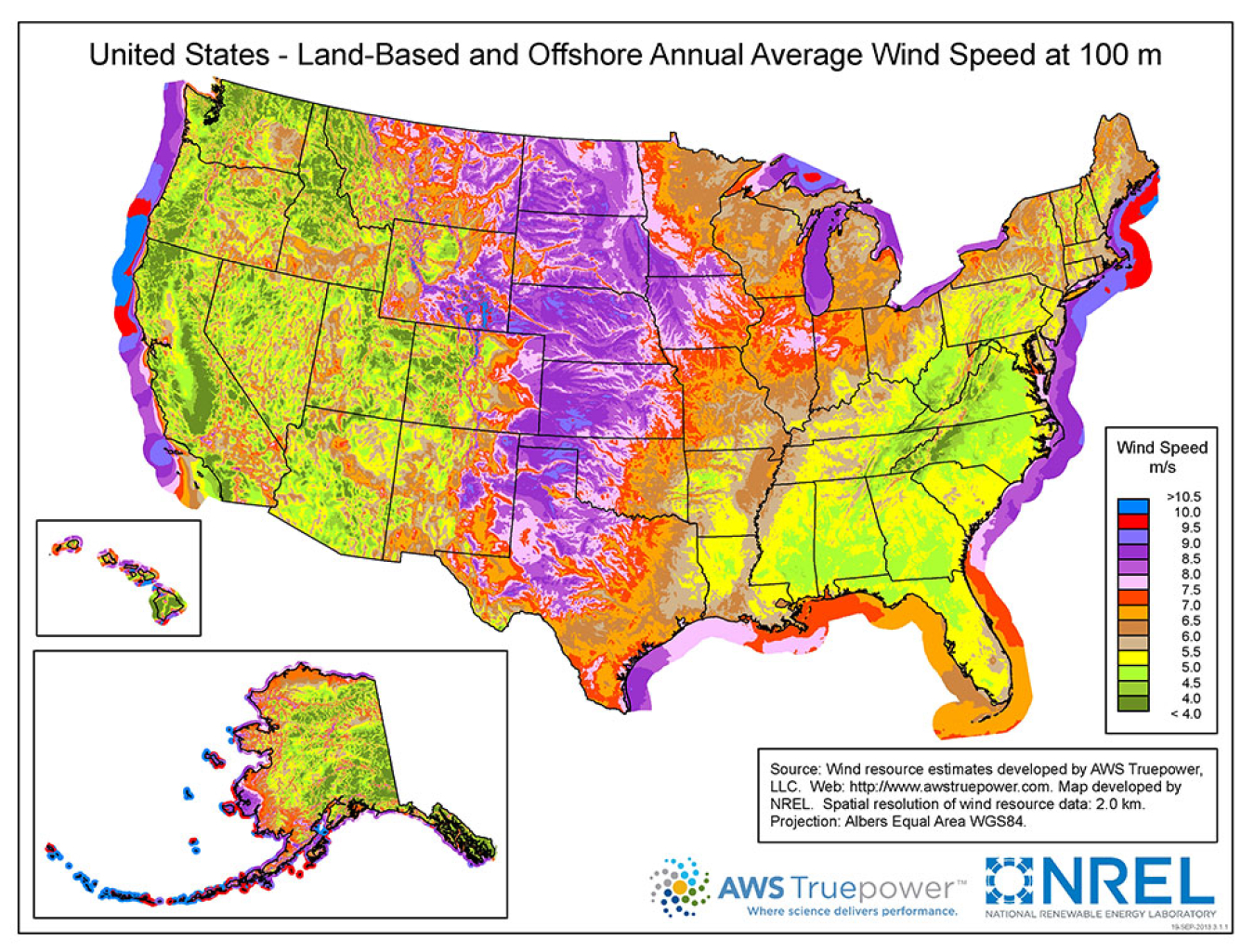

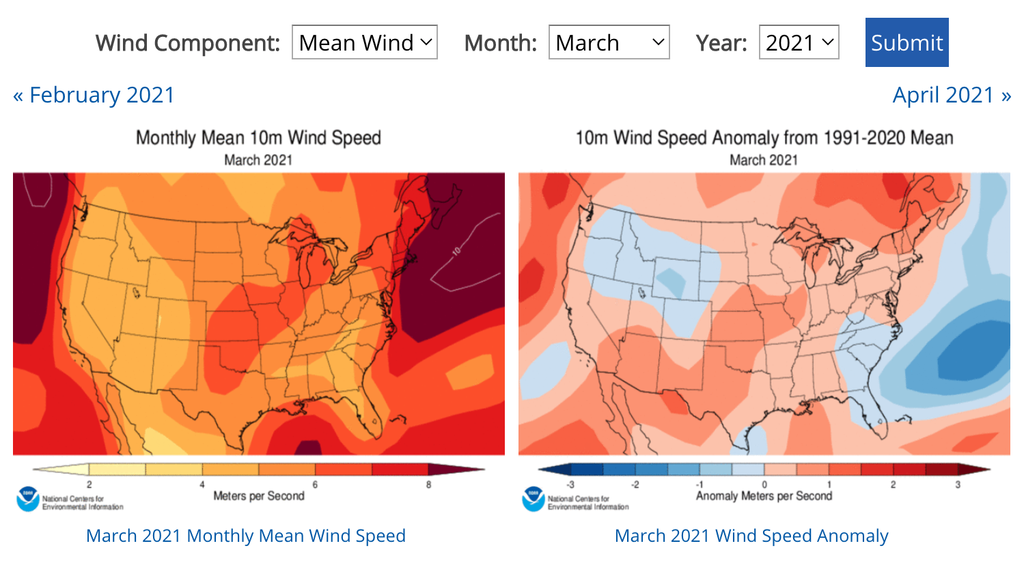

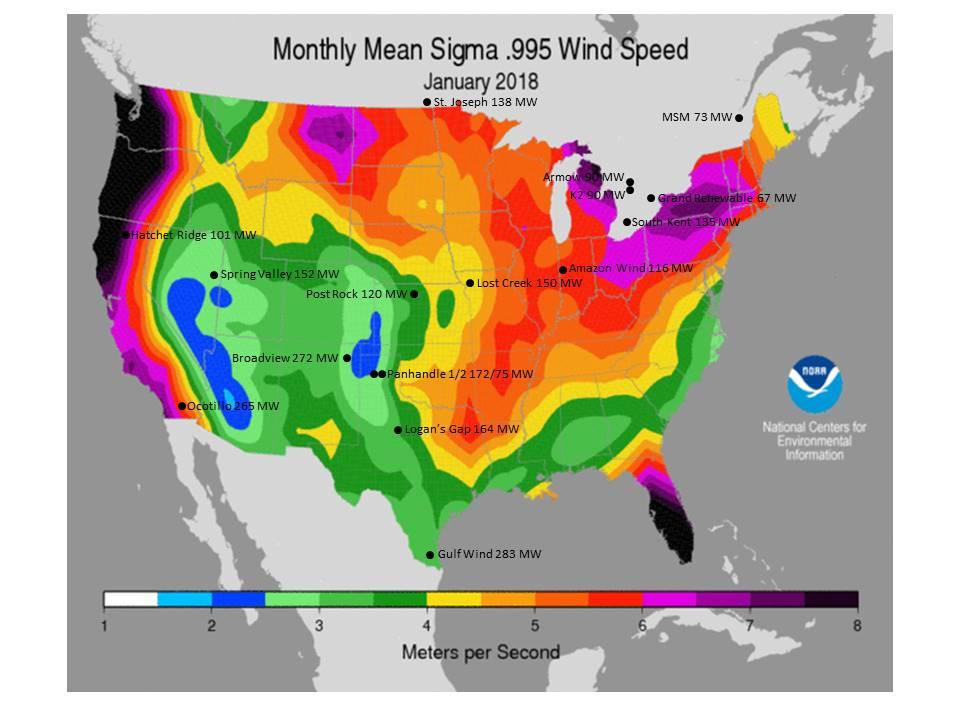

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of the Wind: A Comprehensive Guide to Annual Average Wind Speed Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To South Dakota Plat Maps
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Malaysia: A Geographical Exploration
- Navigating The World Of Digital Maps: A Comprehensive Guide To Purchasing Maps Online
- Unlocking The Secrets Of Malvern, Arkansas: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Map
- Uncovering The Treasures Of Southern Nevada: A Comprehensive Guide To The Caliente Map
- Unraveling The Topography Of Mexico: A Comprehensive Look At The Relief Map
- Navigating The Heart Of History: A Comprehensive Guide To The Athens City Map
- Navigating The Beauty Of Greece: A Guide To Printable Maps
Leave a Reply