Unveiling The World: A Comprehensive Guide To Geographical Maps
Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographical Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographical Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographical Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographical Maps

From ancient cave paintings depicting hunting grounds to intricate digital globes showcasing every corner of our planet, geographical maps have served as indispensable tools for understanding and navigating the world around us. They are visual representations of the Earth’s surface, capturing its physical features, political boundaries, and cultural landscapes. This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of geographical maps, exploring their history, types, construction, applications, and enduring significance in a modern world increasingly reliant on digital technology.
The Genesis of Maps: A Journey Through Time
The origins of maps can be traced back to prehistoric times, with early cave paintings and rock carvings serving as rudimentary depictions of terrain and hunting routes. As civilizations developed, the need for more sophisticated representations of the world grew. Ancient civilizations like the Egyptians, Babylonians, and Greeks employed sophisticated techniques for mapping, using astronomical observations and geometric principles to create accurate representations of their known world.
The Rise of Modern Cartography
The Renaissance ushered in a golden age of cartography, with explorers venturing into uncharted territories and cartographers meticulously documenting their discoveries. The invention of the printing press in the 15th century facilitated the mass production and dissemination of maps, contributing to the spread of geographical knowledge and fostering global exploration.
Types of Maps: A Spectrum of Visual Representations
Geographical maps encompass a diverse range of types, each designed to highlight specific aspects of the Earth’s surface. Here are some prominent examples:
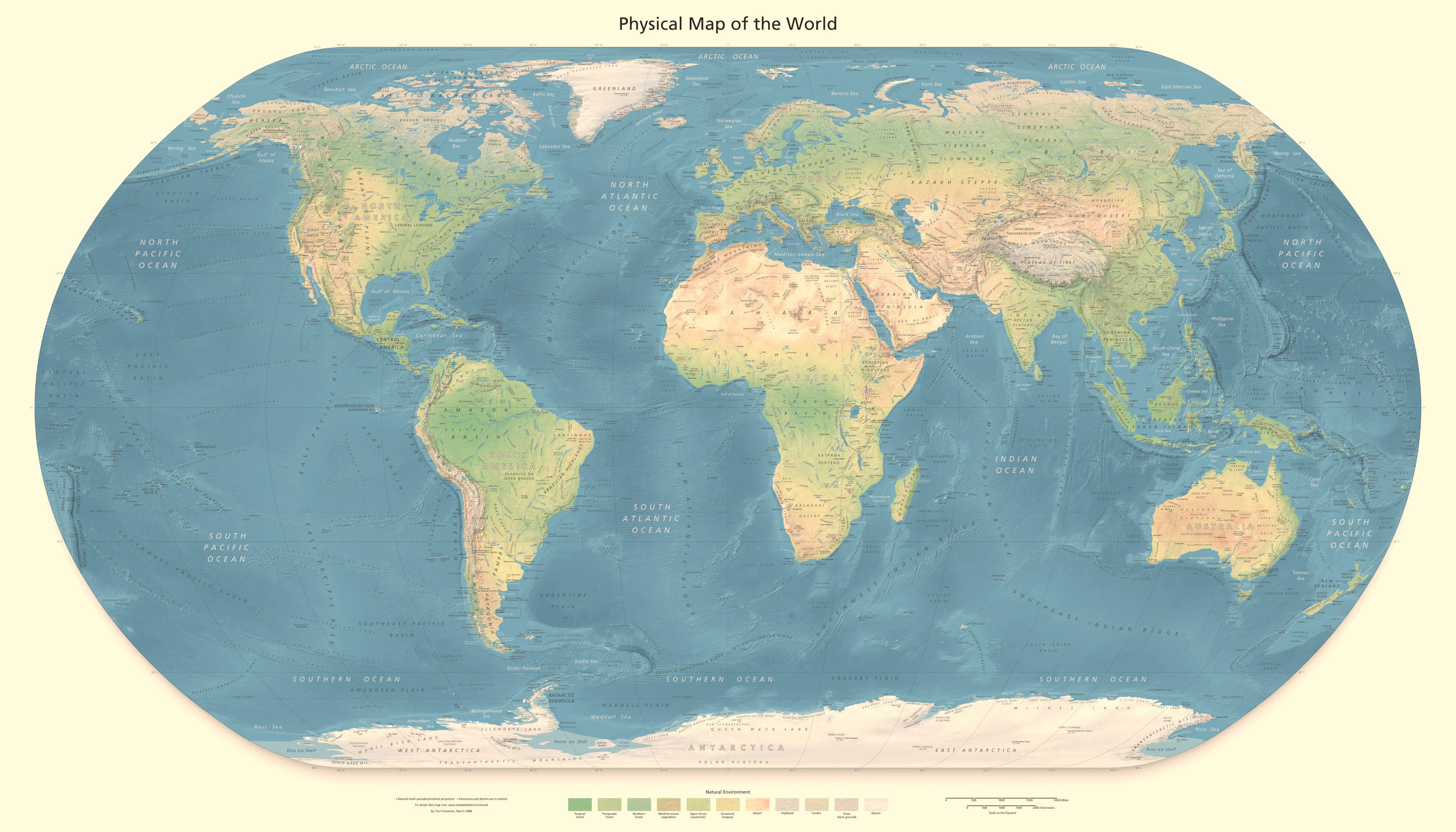
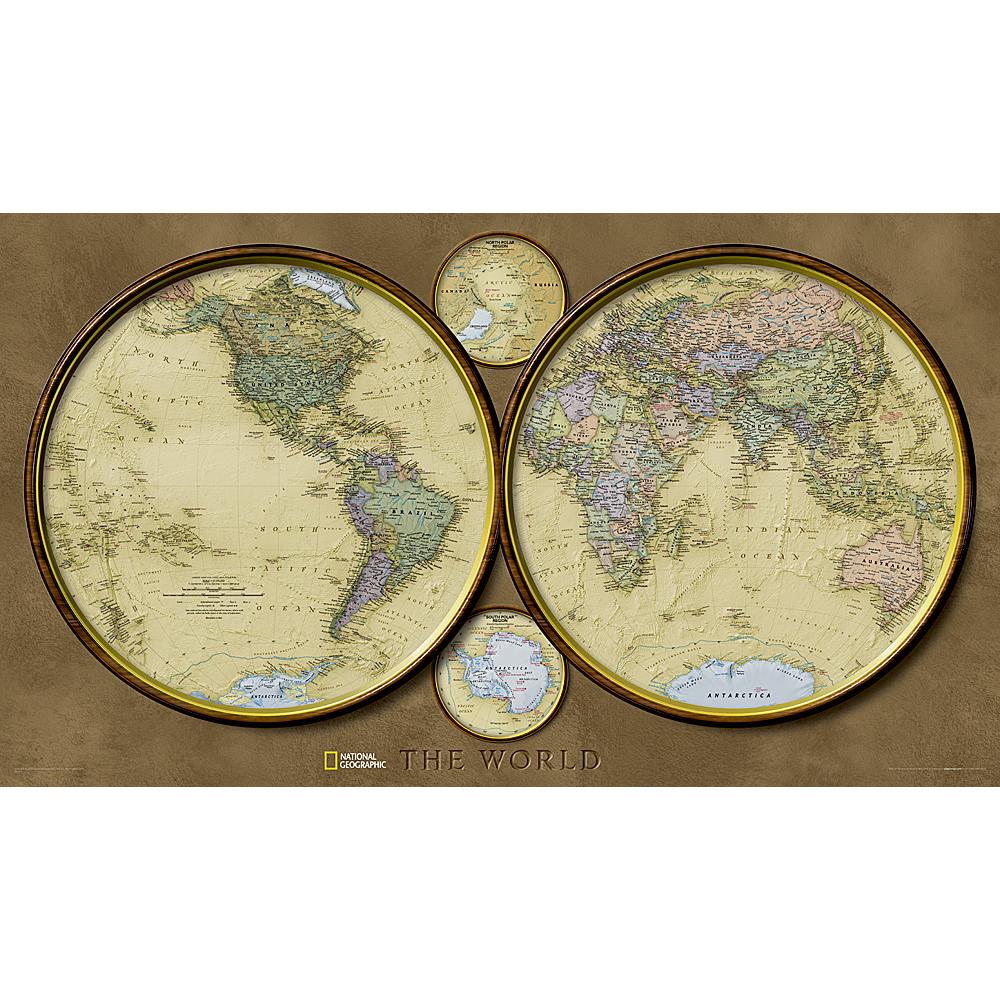
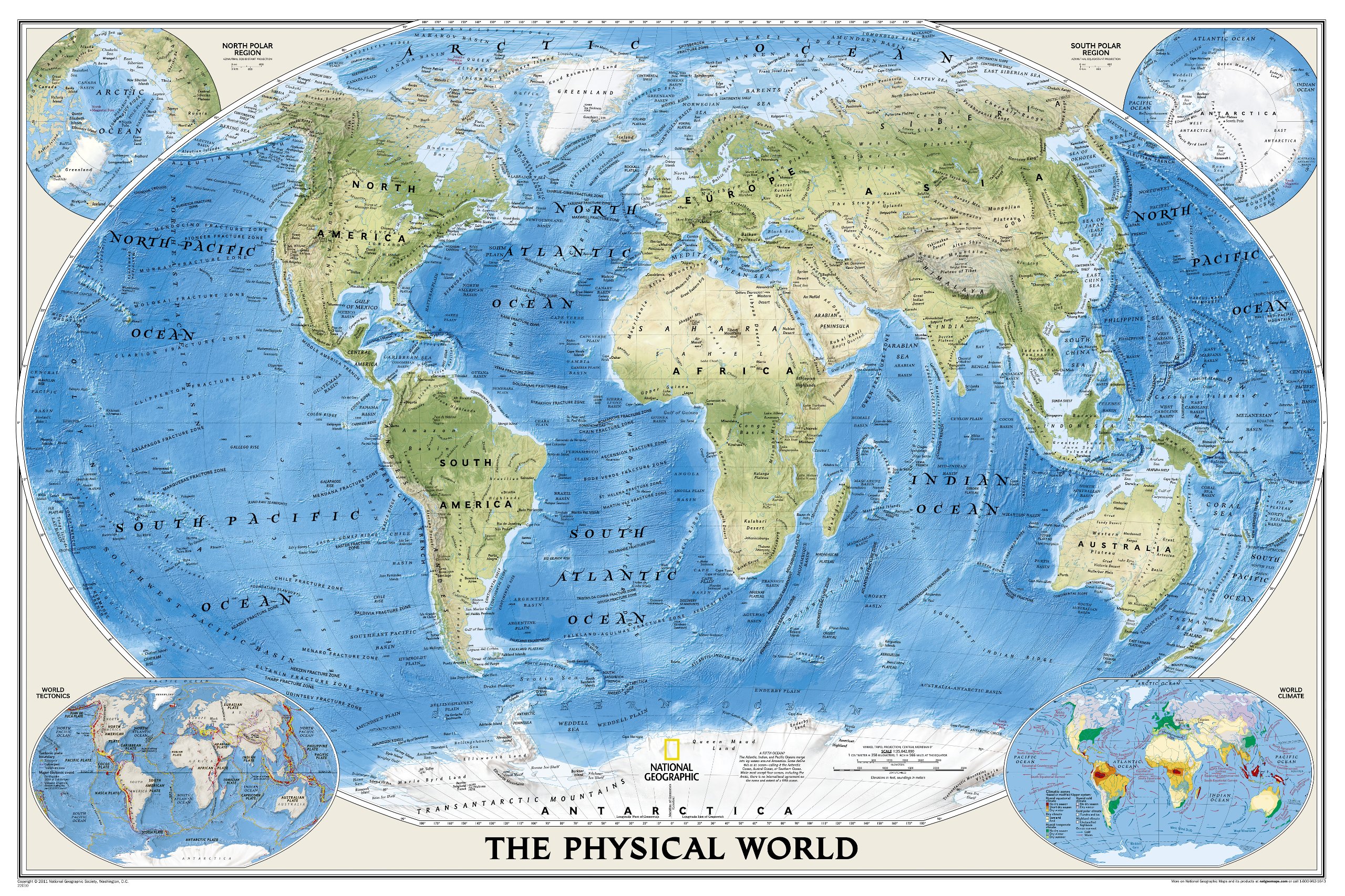
- Reference Maps: These maps serve as fundamental tools for locating places and understanding spatial relationships. They typically depict physical features such as mountains, rivers, and coastlines, along with political boundaries, cities, and roads. Examples include road maps, topographic maps, and world maps.
- Thematic Maps: These maps focus on specific themes or data sets, showcasing patterns, trends, and relationships across geographical regions. Examples include climate maps, population density maps, and economic activity maps.
- Navigation Maps: Designed for guiding travel and navigation, these maps provide detailed information on routes, landmarks, and distances. Examples include nautical charts, aeronautical charts, and GPS maps.
- Historical Maps: These maps depict the historical evolution of geographical features, political boundaries, or population distributions. They offer valuable insights into past events and provide a framework for understanding the present.
The Art and Science of Mapmaking: From Data to Visualization
The creation of a map involves a meticulous process that blends artistic skill with scientific precision. It begins with data collection, which may involve surveying, satellite imagery, or historical records. This data is then processed and analyzed to determine the most relevant information to be presented on the map.
Cartographers employ various techniques for representing the three-dimensional Earth on a two-dimensional surface, using projections, symbols, and scales to maintain accuracy and clarity. Projections involve transforming the Earth’s curved surface onto a flat plane, while symbols represent specific features like cities, roads, or mountains. Scales indicate the relationship between distances on the map and corresponding distances on the Earth’s surface.
The Importance of Maps in a Modern World
Geographical maps continue to play a vital role in our modern world, serving as indispensable tools across diverse disciplines and applications:
- Navigation and Transportation: Maps guide our travel, from navigating city streets to charting long-distance journeys. GPS systems and online mapping services rely on intricate map databases to provide real-time navigation and traffic information.
- Environmental Management: Maps are essential for understanding and managing environmental issues. They help visualize climate change patterns, track deforestation, and monitor pollution levels.
- Urban Planning and Development: Maps provide valuable insights into population distribution, infrastructure networks, and land use patterns, informing urban planning decisions and promoting sustainable development.
- Emergency Response: Maps play a crucial role in coordinating emergency response efforts during natural disasters, providing vital information on evacuation routes, affected areas, and resource distribution.
- Historical Research and Education: Historical maps provide valuable insights into past societies, their cultures, and their interactions with the environment. They serve as crucial tools for historical research and education, helping us understand the evolution of human civilization.
The Future of Maps: Embracing Digital Innovation
The digital revolution has profoundly impacted the world of maps, ushering in a new era of interactive, dynamic, and data-rich representations of the Earth’s surface. Online mapping platforms like Google Maps and OpenStreetMap offer real-time traffic updates, street view imagery, and personalized navigation features.
Furthermore, the integration of geographic information systems (GIS) with mapping technologies has enabled the creation of sophisticated data visualization tools that facilitate complex spatial analysis and decision-making.
FAQs: Demystifying the World of Maps
1. What are the different types of projections used in mapmaking?
Projections are mathematical techniques used to transform the Earth’s curved surface onto a flat plane. Common projections include Mercator, Lambert Conformal Conic, and Transverse Mercator, each with its own strengths and weaknesses in terms of preserving shape, area, or distance.
2. What is the difference between a map scale and a map legend?
A map scale indicates the relationship between distances on the map and corresponding distances on the Earth’s surface. It can be expressed as a ratio, a verbal statement, or a graphic scale. A map legend explains the symbols used on the map, providing information on what each symbol represents.
3. How can I create my own map?
Creating a map requires a combination of data collection, software tools, and cartographic skills. Online mapping platforms like Google My Maps and ArcGIS Online offer user-friendly interfaces for creating custom maps.
4. What are some ethical considerations in mapmaking?
Mapmaking involves ethical considerations related to data accuracy, representation of different cultures, and potential biases that may be embedded in the map’s design and interpretation.
5. What are the benefits of using digital maps over traditional paper maps?
Digital maps offer numerous advantages over traditional paper maps, including interactivity, real-time updates, personalized navigation features, and access to a wide range of data layers.
Tips for Understanding and Using Maps
- Pay attention to the map’s scale: Understand the relationship between distances on the map and the real world to accurately interpret distances and areas.
- Examine the map’s legend: Familiarize yourself with the symbols used on the map to understand the information being presented.
- Consider the map’s projection: Be aware of the projection used in the map, as it can affect the accuracy of shape, area, or distance.
- Use multiple maps for different purposes: Utilize different types of maps to gain a comprehensive understanding of a particular area or theme.
- Explore online mapping platforms: Utilize interactive mapping tools to gain insights into real-time data, traffic conditions, and personalized navigation options.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Maps
Geographical maps have evolved from rudimentary depictions of the world to sophisticated data visualization tools that empower us to understand, navigate, and manage our planet. They serve as essential tools for exploration, navigation, environmental management, urban planning, and historical research. As technology continues to advance, the future of maps promises even greater interactivity, data richness, and personalized experiences, further enhancing our understanding and interaction with the world around us.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographical Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- Navigating The Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To South Dakota Plat Maps
- Navigating The Tapestry Of Malaysia: A Geographical Exploration
- Navigating The World Of Digital Maps: A Comprehensive Guide To Purchasing Maps Online
- Unlocking The Secrets Of Malvern, Arkansas: A Comprehensive Guide To The City’s Map
- Uncovering The Treasures Of Southern Nevada: A Comprehensive Guide To The Caliente Map
- Unraveling The Topography Of Mexico: A Comprehensive Look At The Relief Map
- Navigating The Heart Of History: A Comprehensive Guide To The Athens City Map
- Navigating The Beauty Of Greece: A Guide To Printable Maps
Leave a Reply